Dinosaur Footprints: Traces of the Ancient Past
Date:2024/07/31 Visits:1974
 Dinosaur footprints, also known as trace fossils or ichnites, offer a fascinating glimpse into the lives of these ancient creatures. Unlike body fossils, which are the remains of the animal itself, trace fossils are the preserved evidence of the activities of organisms. Dinosaur footprints provide crucial information about dinosaur behavior, movement, and even their environment. In this article, we will explore the significance of dinosaur footprints, the process of their formation, notable discoveries, and their role in modern paleontology.
Dinosaur footprints, also known as trace fossils or ichnites, offer a fascinating glimpse into the lives of these ancient creatures. Unlike body fossils, which are the remains of the animal itself, trace fossils are the preserved evidence of the activities of organisms. Dinosaur footprints provide crucial information about dinosaur behavior, movement, and even their environment. In this article, we will explore the significance of dinosaur footprints, the process of their formation, notable discoveries, and their role in modern paleontology.
The Significance of Dinosaur Footprints
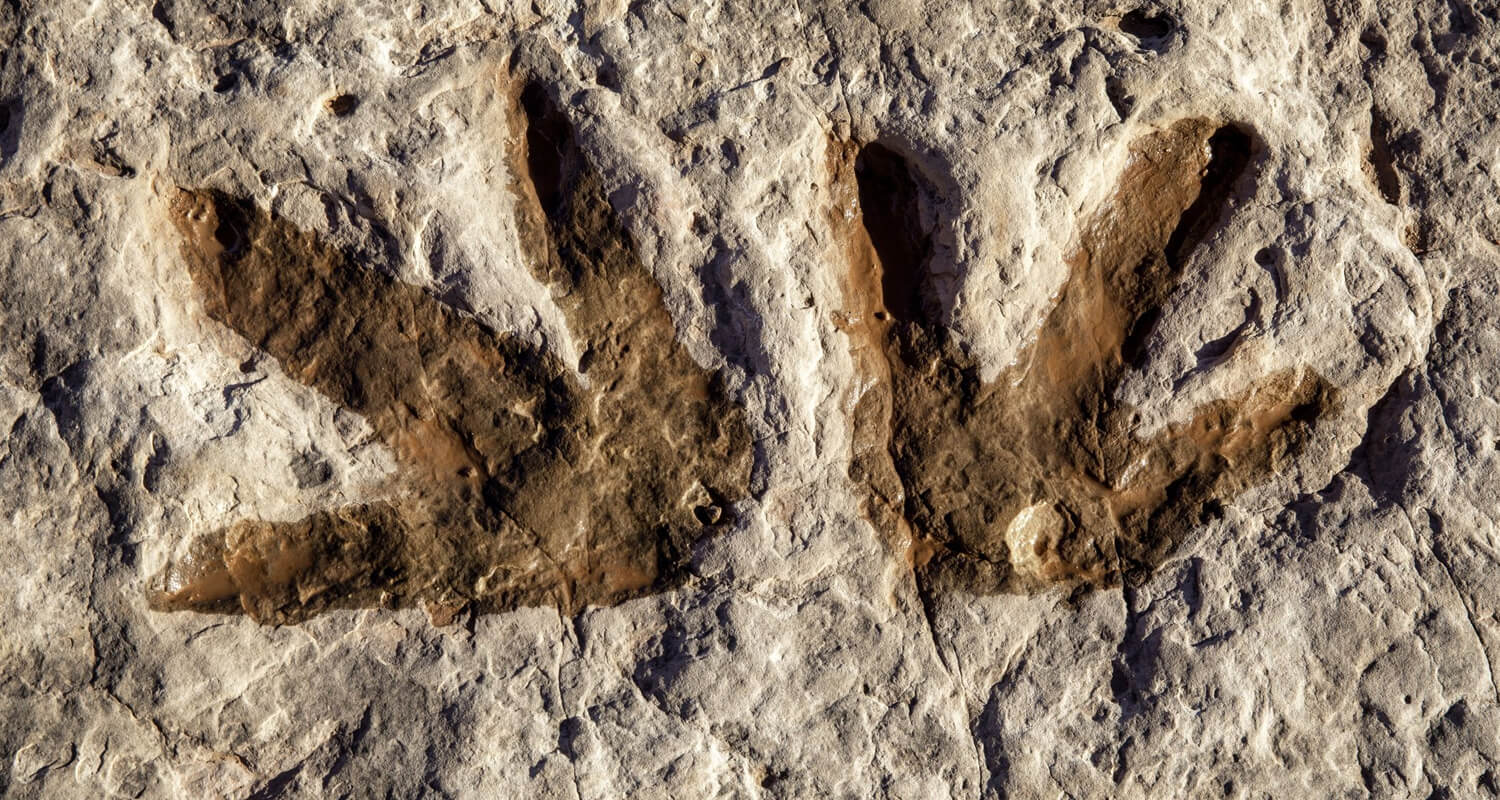 Dinosaur footprints are invaluable to scientists because they can reveal details about the dinosaur's size, gait, speed, and even social behavior. By studying the size and depth of footprints, paleontologists can estimate the dinosaur's weight and the type of terrain they traversed. Trackways, which are a series of footprints, can indicate whether dinosaurs traveled alone or in groups, providing insights into their social structure.
Dinosaur footprints are invaluable to scientists because they can reveal details about the dinosaur's size, gait, speed, and even social behavior. By studying the size and depth of footprints, paleontologists can estimate the dinosaur's weight and the type of terrain they traversed. Trackways, which are a series of footprints, can indicate whether dinosaurs traveled alone or in groups, providing insights into their social structure.
Key Insights from Dinosaur Footprints
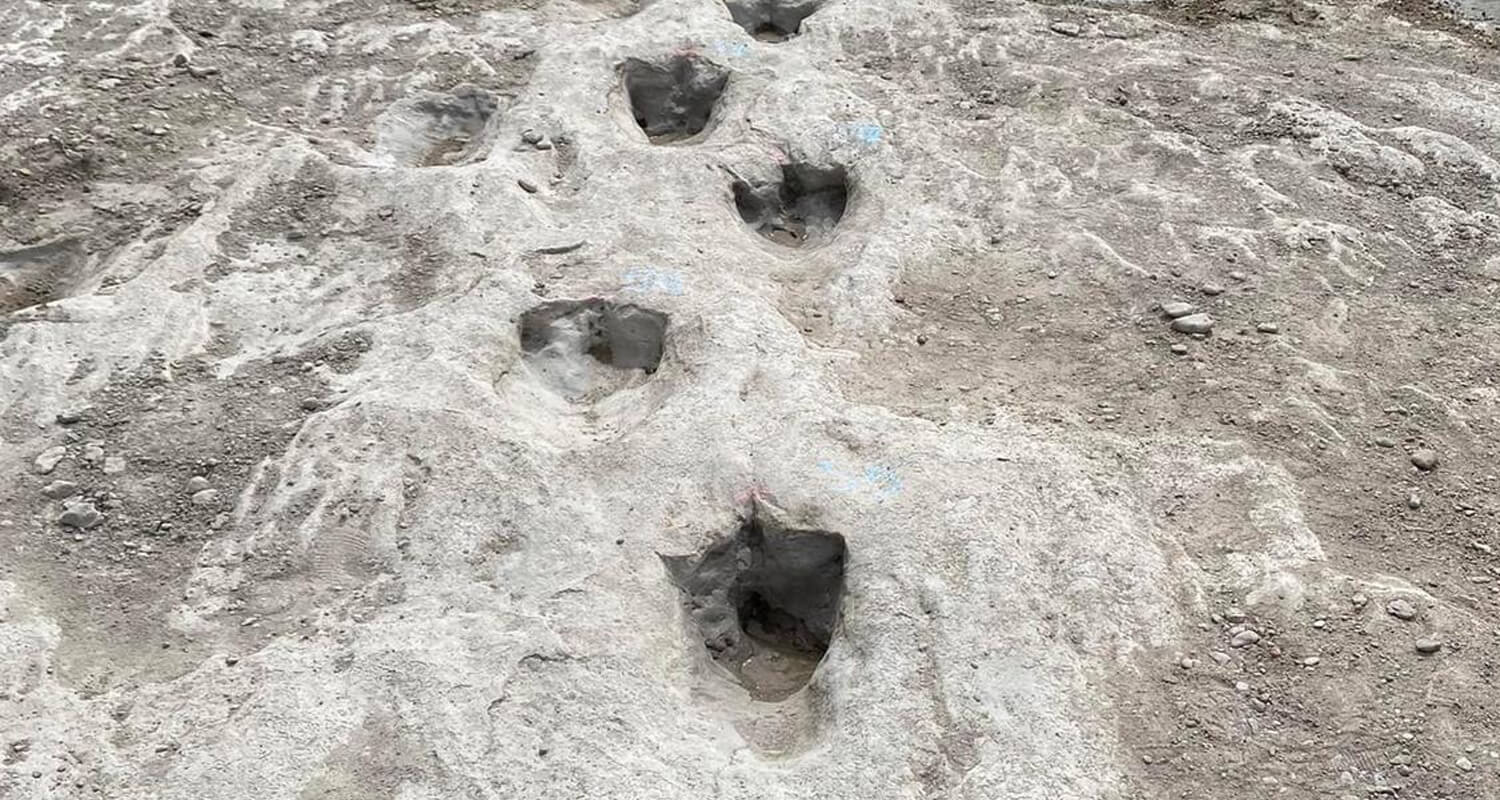

Behavioral Patterns: Footprints can suggest whether a dinosaur was walking, running, or resting. For example, closely spaced footprints may indicate a slow, deliberate movement, while widely spaced prints could imply a rapid pace or running.
Social Behavior: Multiple trackways found together can indicate herd behavior or social interactions among dinosaurs.
Environmental Clues: The type of sediment in which the footprints are found can provide information about the ancient environment, such as whether it was a floodplain, desert, or coastal area.
How Dinosaur Footprints Form
 Dinosaur footprints are formed when dinosaurs walk across soft, pliable surfaces like mud, sand, or silt. These impressions are then buried by additional sediment layers. Over time, the sediment hardens into rock, preserving the footprints. Key factors in the formation of dinosaur footprints include:
Dinosaur footprints are formed when dinosaurs walk across soft, pliable surfaces like mud, sand, or silt. These impressions are then buried by additional sediment layers. Over time, the sediment hardens into rock, preserving the footprints. Key factors in the formation of dinosaur footprints include:
Substrate Consistency: The ground must be soft enough to capture the footprint's details but firm enough to hold the impression until it is covered by sediment.
Rapid Burial: Quick burial by sediment helps protect the footprints from erosion and weathering.
Sediment Composition: Fine-grained sediments like mud and silt are more likely to preserve detailed footprints.
Notable Dinosaur Footprint Discoveries
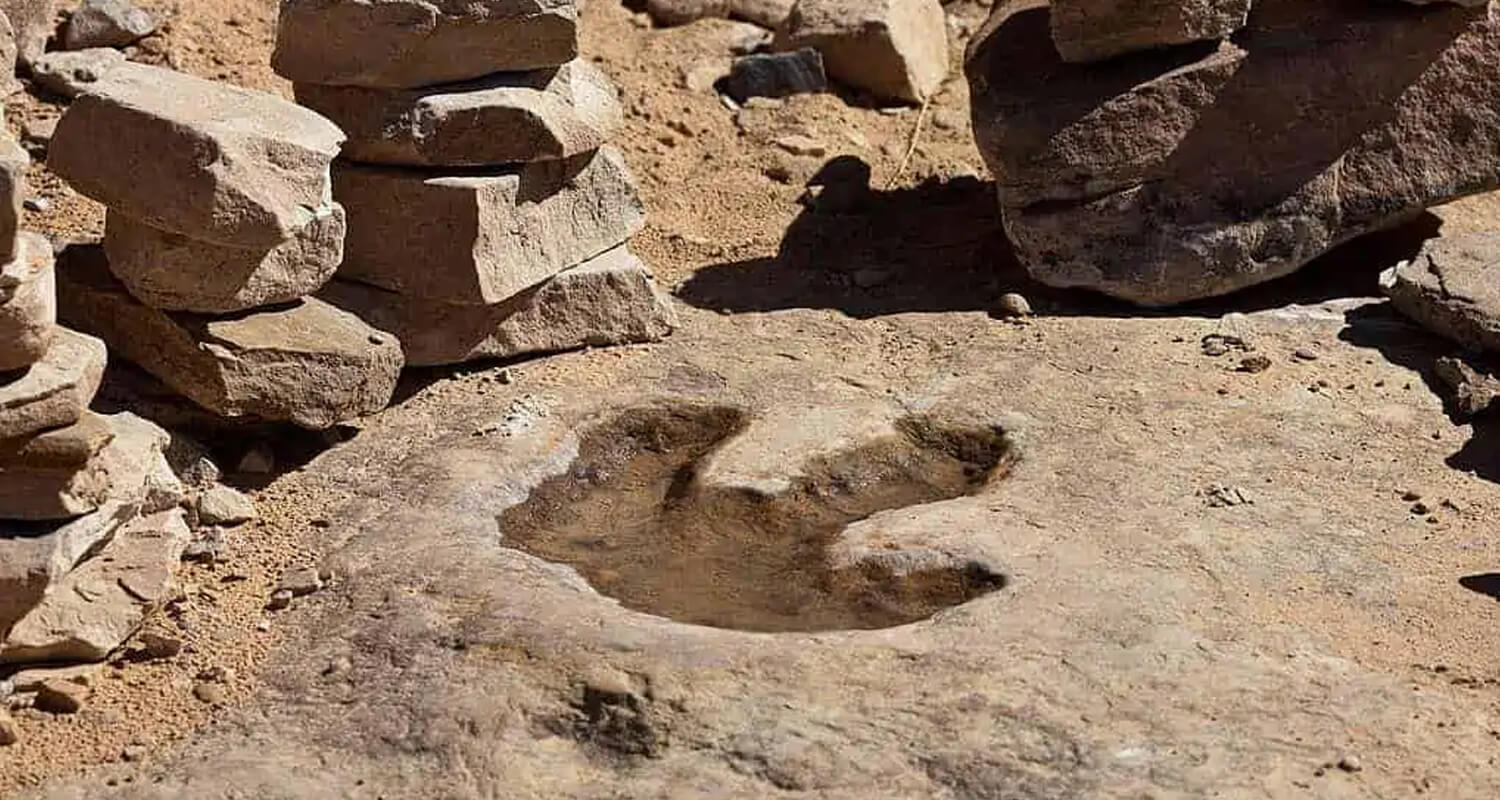 Several significant dinosaur footprint discoveries have provided valuable insights into the behavior and environment of these ancient animals.
Several significant dinosaur footprint discoveries have provided valuable insights into the behavior and environment of these ancient animals.
Examples of Notable Discoveries
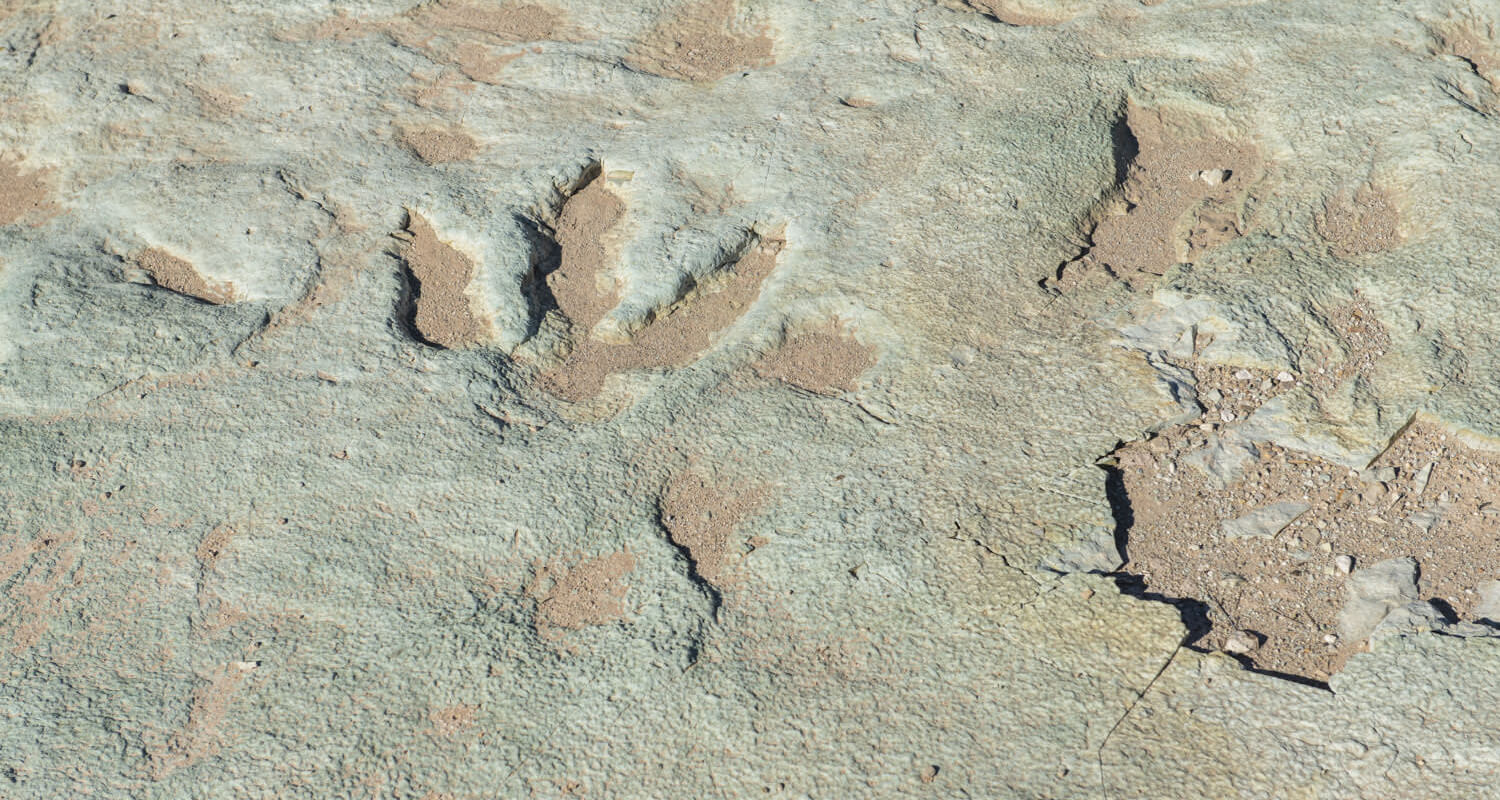

Paluxy River, Texas: Famous for its well-preserved trackways of theropods and sauropods, suggesting interactions between different dinosaur species.
Dinosaur Ridge, Colorado: A site with numerous footprints that provide evidence of both bipedal and quadrupedal dinosaurs.
La Rioja, Spain: Home to some of the best-preserved dinosaur footprints, offering a glimpse into the behavior of various dinosaur species, including theropods, ornithopods, and sauropods.
Dinosaur Footprints in Modern Paleontology
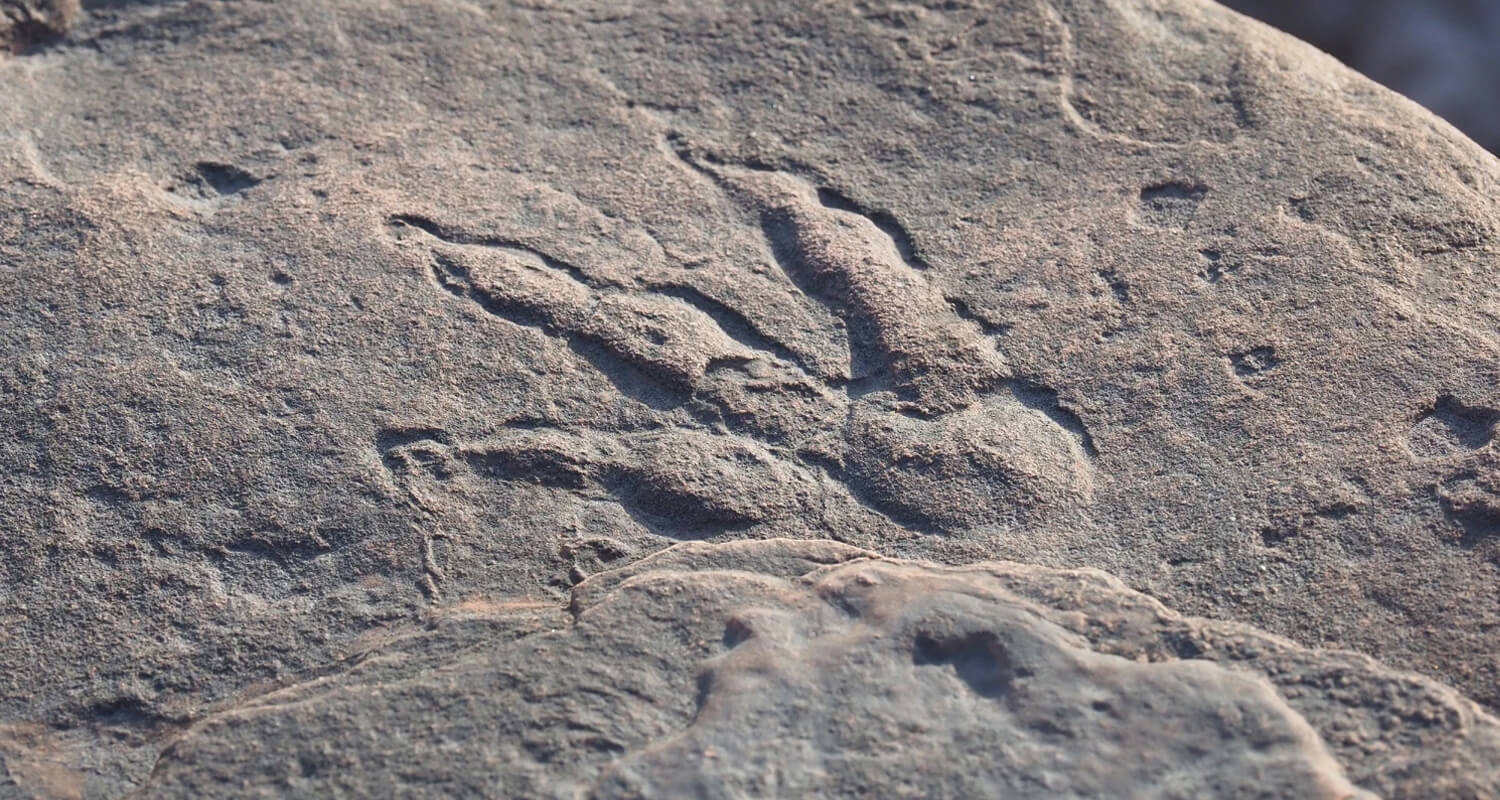 Modern paleontologists use advanced techniques to study dinosaur footprints, including 3D scanning and computer modeling. These methods allow for detailed analysis of footprint morphology and enable scientists to create digital reconstructions of dinosaur trackways. Such technology has revolutionized the study of ichnology (the study of trace fossils), providing new insights into dinosaur locomotion and behavior.
Modern paleontologists use advanced techniques to study dinosaur footprints, including 3D scanning and computer modeling. These methods allow for detailed analysis of footprint morphology and enable scientists to create digital reconstructions of dinosaur trackways. Such technology has revolutionized the study of ichnology (the study of trace fossils), providing new insights into dinosaur locomotion and behavior.
Applications in Paleontology
Reconstructing Movement: By analyzing the depth, angle, and spacing of footprints, scientists can reconstruct how dinosaurs moved, including their walking and running patterns.
Estimating Speed: Trackway measurements can help estimate the speed at which dinosaurs traveled, providing clues about their hunting and escaping behaviors.
Understanding Behavior: Detailed footprint analysis can reveal social behaviors, such as whether dinosaurs moved in herds or had specific migratory patterns.
FAQs About Dinosaur Footprints
 Q: How are dinosaur footprints preserved?
Q: How are dinosaur footprints preserved?
A: Dinosaur footprints are preserved when dinosaurs walk on soft sediment, which is then quickly buried by additional layers of sediment. Over time, the sediment hardens into rock, preserving the footprints.
Q: What can dinosaur footprints tell us about dinosaur behavior?
A: Footprints can reveal information about dinosaur size, gait, speed, and social behavior. Trackways can indicate whether dinosaurs traveled alone or in groups.
Q: Where can I see dinosaur footprints?
A: Dinosaur footprints can be seen at various fossil sites and museums around the world, including the Paluxy River in Texas, Dinosaur Ridge in Colorado, and La Rioja in Spain.
Q: How do scientists study dinosaur footprints?
A: Scientists use techniques like 3D scanning and computer modeling to analyze the morphology of footprints. These methods help reconstruct dinosaur movement and behavior.
Q: Are all dinosaur footprints the same?
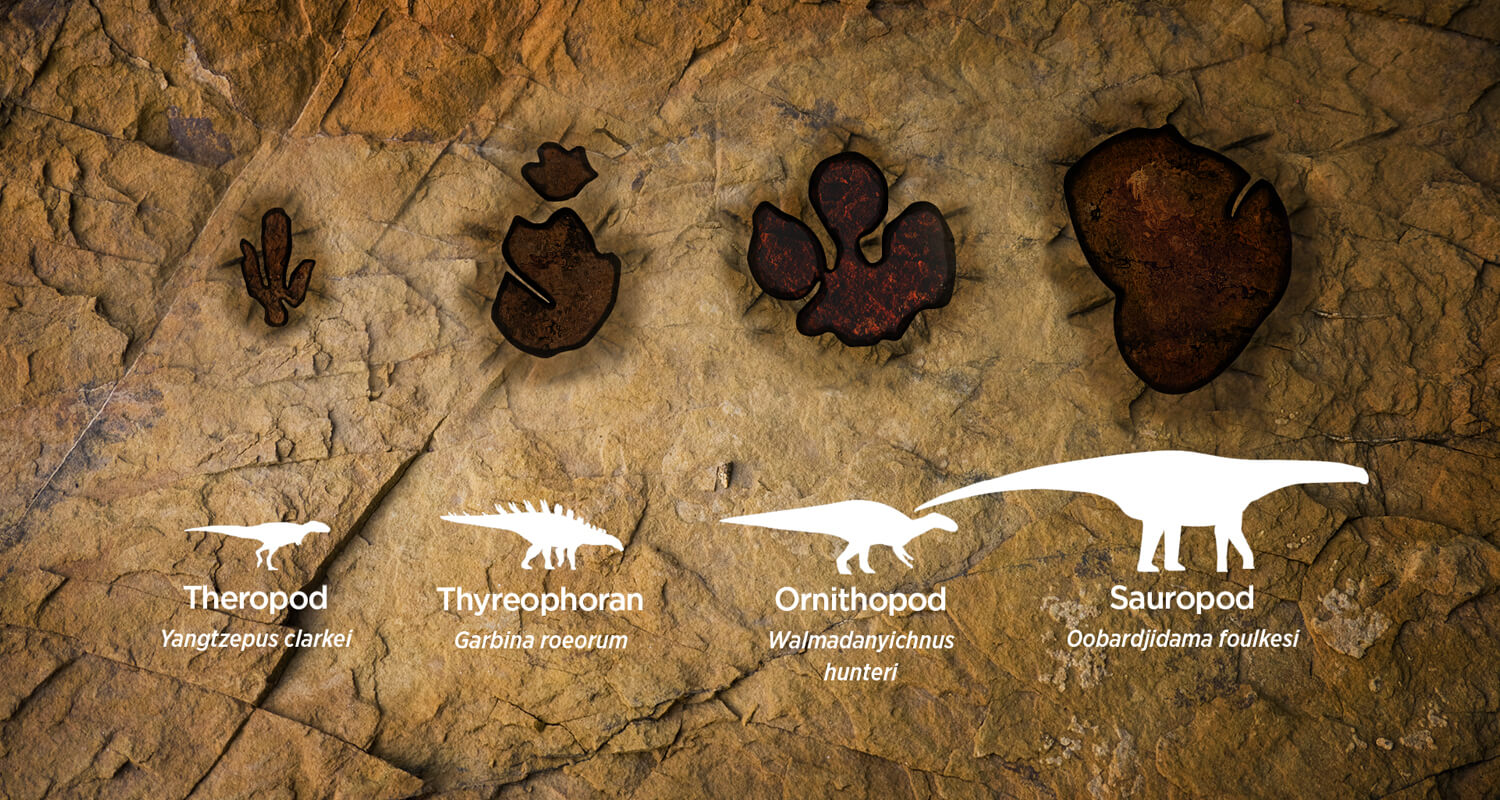
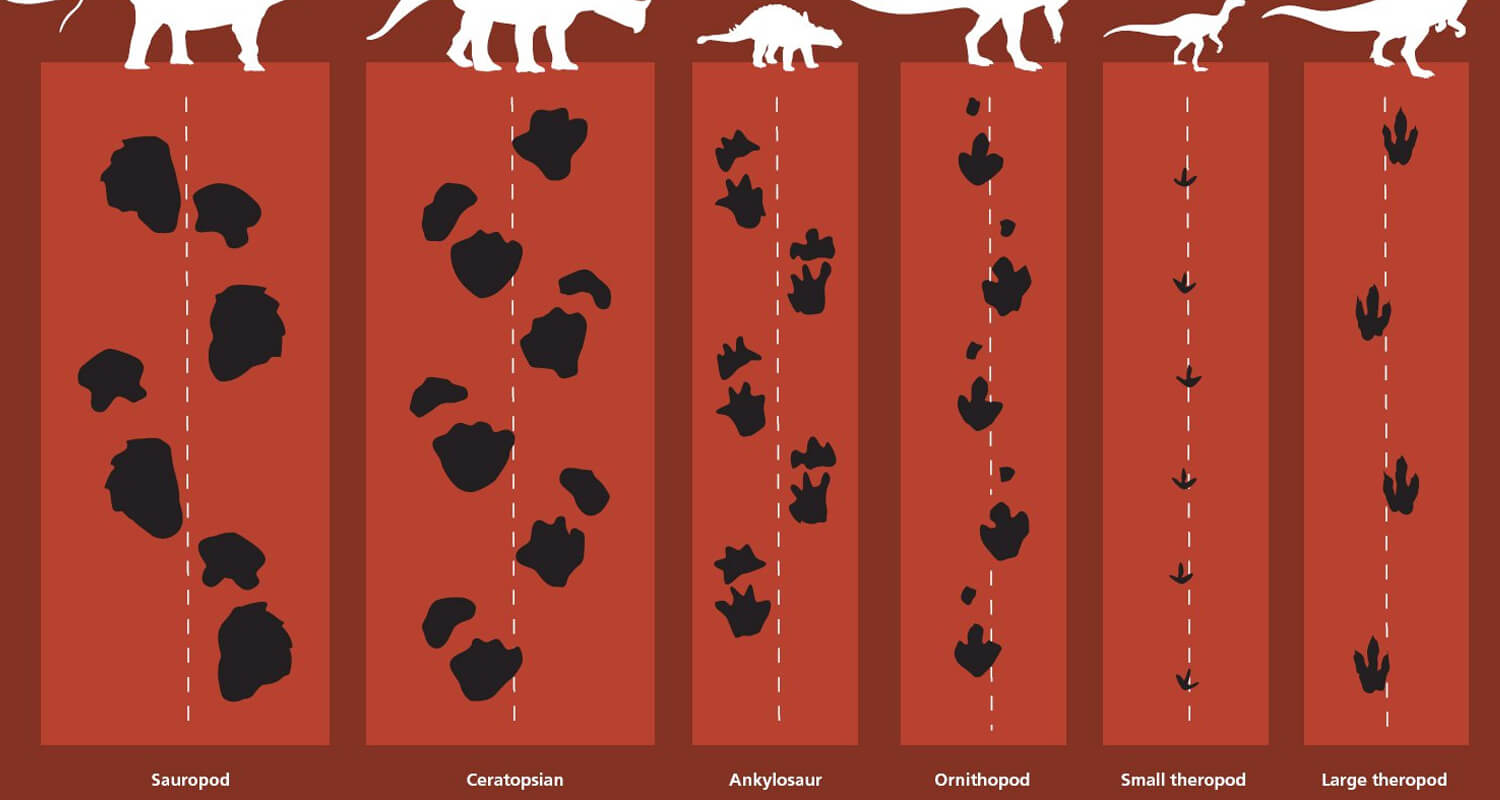
A: No, dinosaur footprints vary depending on the species, size, and type of movement. Different types of dinosaurs, such as theropods, sauropods, and ornithopods, leave distinct footprints.
Conclusion
 Dinosaur footprints are more than just ancient marks in the rock; they are windows into the lives of creatures that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. By studying these trace fossils, paleontologists can uncover valuable information about dinosaur behavior, movement, and environments. As technology continues to advance, our understanding of these prehistoric giants will only deepen, offering even more intriguing insights into the ancient past.
Dinosaur footprints are more than just ancient marks in the rock; they are windows into the lives of creatures that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. By studying these trace fossils, paleontologists can uncover valuable information about dinosaur behavior, movement, and environments. As technology continues to advance, our understanding of these prehistoric giants will only deepen, offering even more intriguing insights into the ancient past.












