What Did Dinosaurs Eat? A Look at Prehistoric Diets
Date:2024/12/18 Visits:3315
 Dinosaurs, the fascinating giants of the Mesozoic era, exhibited remarkable diversity in size, shape, and behavior. One of the most intriguing aspects of their lives was their diet, which ranged from plants to meat and everything in between. By examining what dinosaurs ate, we gain insight into their ecosystems and how they survived and thrived millions of years ago.
Dinosaurs, the fascinating giants of the Mesozoic era, exhibited remarkable diversity in size, shape, and behavior. One of the most intriguing aspects of their lives was their diet, which ranged from plants to meat and everything in between. By examining what dinosaurs ate, we gain insight into their ecosystems and how they survived and thrived millions of years ago.
How Do Scientists Determine Dinosaur Diets?
 Understanding the diets of dinosaurs is no easy task, but paleontologists use several methods to uncover clues:
Understanding the diets of dinosaurs is no easy task, but paleontologists use several methods to uncover clues:
Fossilized Teeth and Jaw Structures: The shape, size, and wear patterns of teeth offer vital clues. Sharp, serrated teeth often indicate a carnivorous diet, while flat, ridged teeth suggest plant-eating habits.
Fossilized Stomach Contents and Coprolites: Occasionally, fossilized remains of a dinosaur's last meal or dung provide direct evidence of their diet.
Skeletal Anatomy and Paleoenvironment: The structure of a dinosaur's body and the environment they lived in help scientists infer feeding behaviors. For example, long-necked dinosaurs likely fed on high vegetation.
Herbivorous Dinosaurs: Plant Eaters of the Mesozoic
 Herbivorous dinosaurs were the primary consumers of the lush vegetation that dominated the Mesozoic landscape. Their diets included ferns, cycads, conifers, and flowering plants that emerged in the later periods.
Herbivorous dinosaurs were the primary consumers of the lush vegetation that dominated the Mesozoic landscape. Their diets included ferns, cycads, conifers, and flowering plants that emerged in the later periods.
Notable Herbivorous Dinosaurs
Sauropods: Giants like Brachiosaurus and Diplodocus used their long necks to graze on tall trees. Their peg-like teeth were ideal for stripping foliage but not for chewing.
Ornithischians: Dinosaurs such as Triceratops and Stegosaurus fed on lower vegetation. Triceratops used its beak to clip tough plants, while Stegosaurus relied on its small, flat teeth to process soft vegetation.
Adaptations for Eating Plants
Herbivores developed tools for efficient feeding, such as sharp beaks for cutting, specialized teeth for grinding, and even gizzard stones to aid in digesting tough plant material.
Carnivorous Dinosaurs: Meat Eaters and Apex Predators
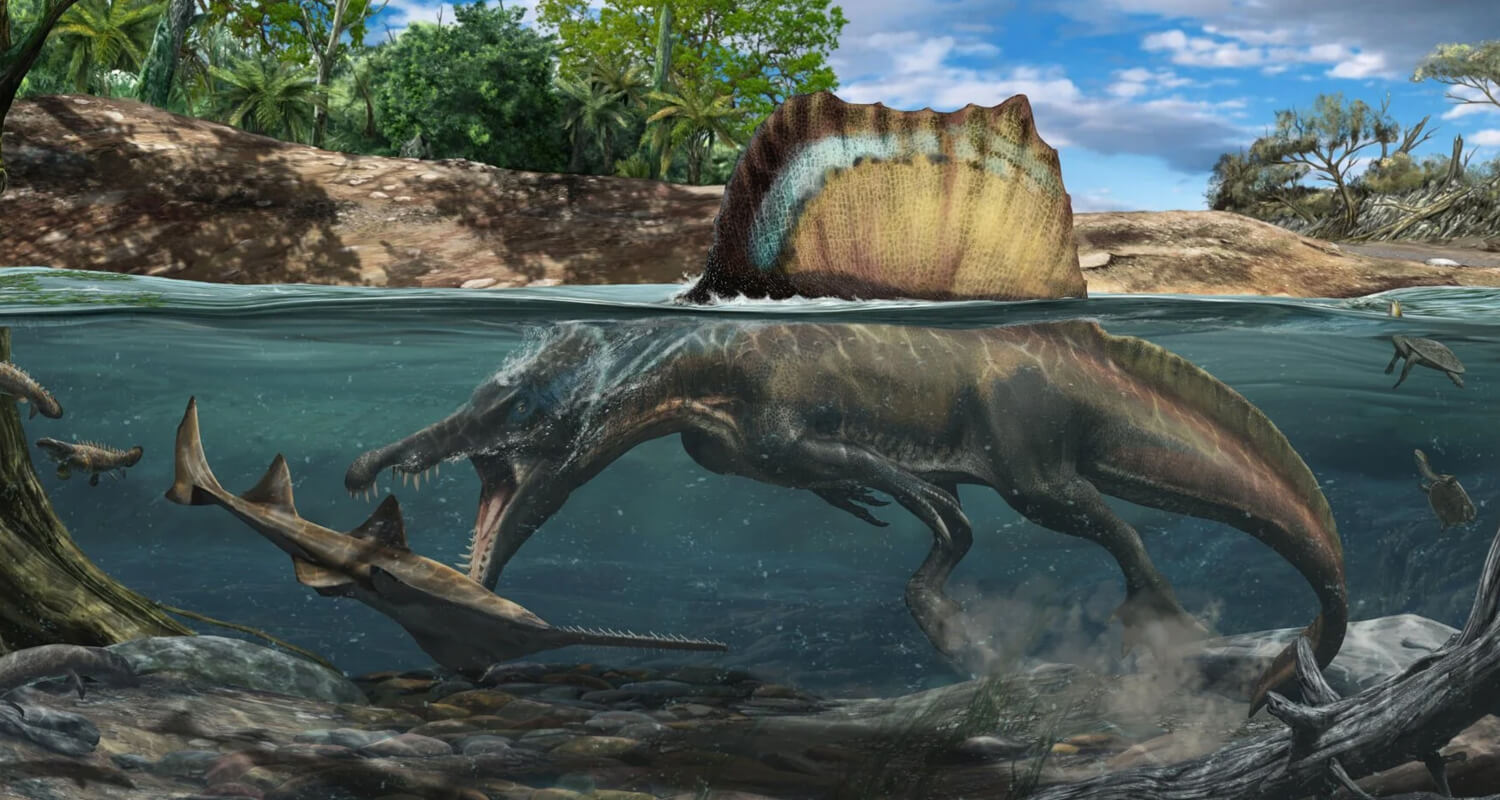 Carnivorous dinosaurs occupied the top of the food chain, preying on herbivores and scavenging when necessary.
Carnivorous dinosaurs occupied the top of the food chain, preying on herbivores and scavenging when necessary.
Iconic Carnivorous Dinosaurs
Tyrannosaurus Rex: Known for its crushing bite, T. rex hunted large herbivores and scavenged carcasses. Its massive teeth could break through bone.
Velociraptor: Smaller but highly agile, Velociraptors were likely pack hunters that used their sharp claws to subdue prey.
Adaptations for Hunting
Carnivores evolved sharp teeth, powerful jaws, and strong limbs for capturing and consuming prey. Their agility and speed made them formidable hunters.
Omnivorous Dinosaurs: A Flexible Approach to Eating
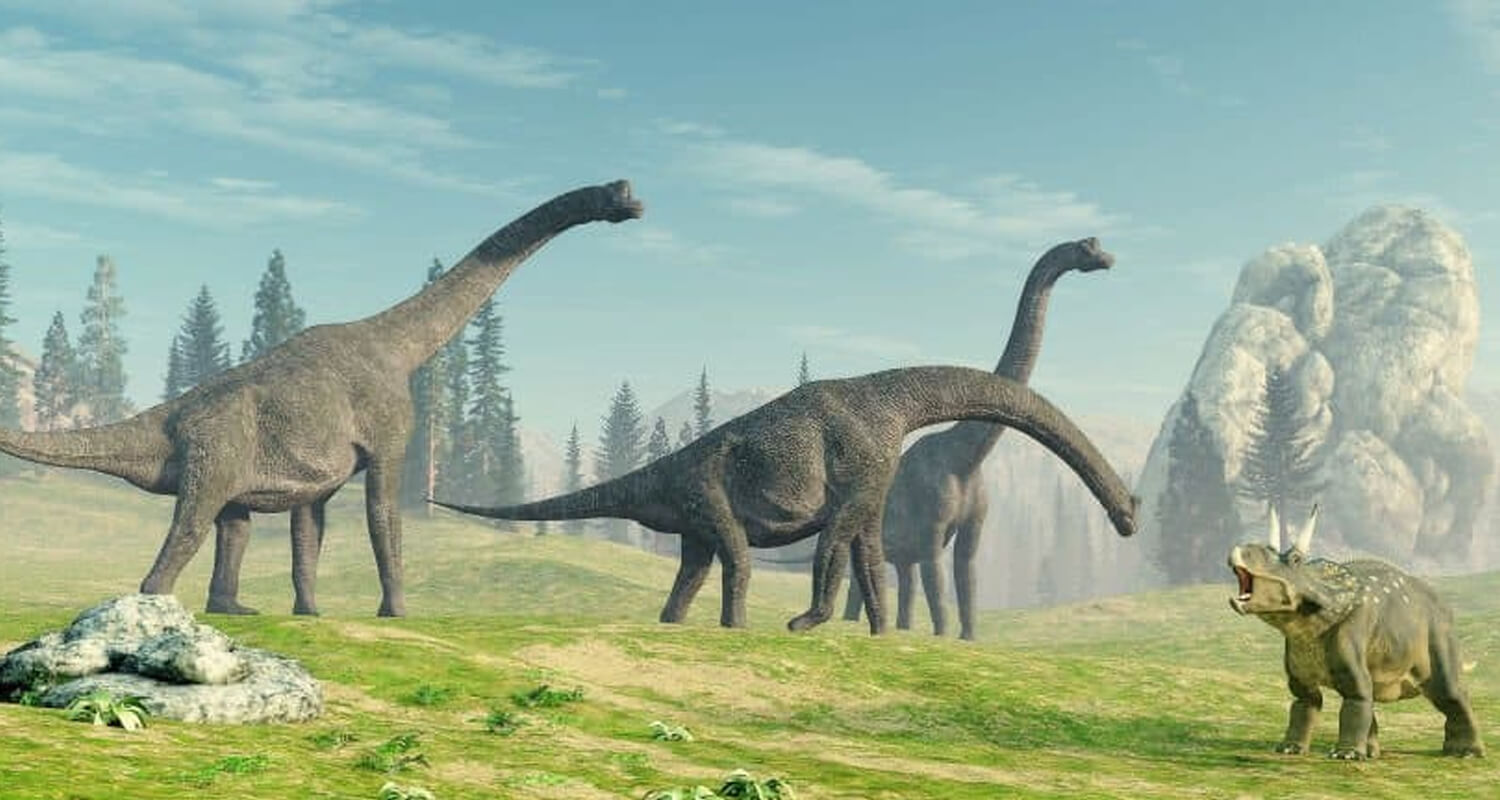 Omnivorous dinosaurs combined the best of both worlds, eating plants, small animals, and insects.
Omnivorous dinosaurs combined the best of both worlds, eating plants, small animals, and insects.
Examples of Omnivorous Dinosaurs
Oviraptor: Despite its name meaning “egg thief,” Oviraptor likely had a varied diet of seeds, plants, and small prey.
Troodon: With a large brain for its size, Troodon may have used its intelligence to exploit a wide range of food sources.
Advantages of Omnivory
Being dietary generalists allowed these dinosaurs to adapt to changing environments and resource availability, increasing their chances of survival.
Specialized Dinosaurs and Unique Feeding Habits
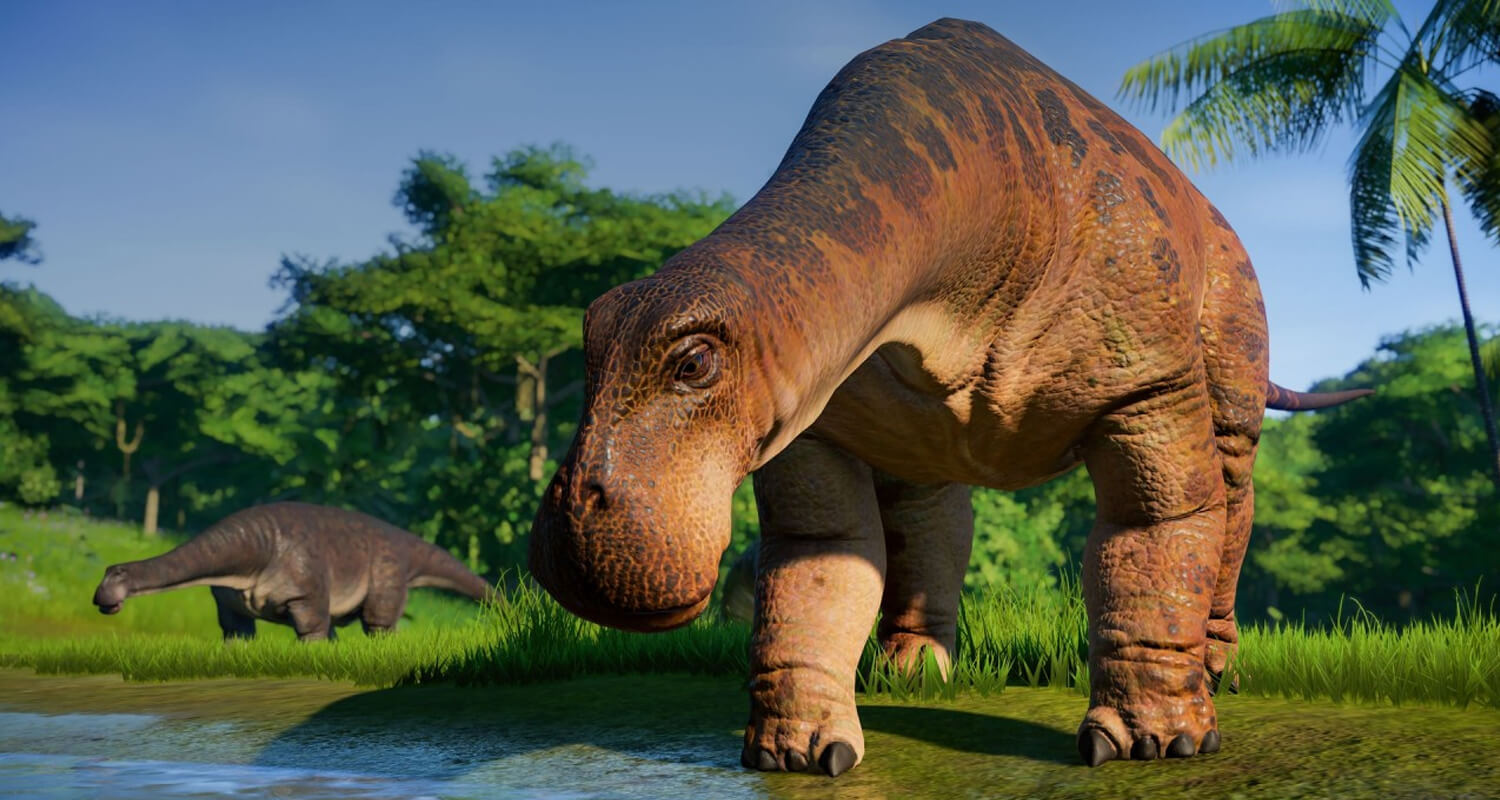 Some dinosaurs developed highly specialized diets tailored to their environments:
Some dinosaurs developed highly specialized diets tailored to their environments:
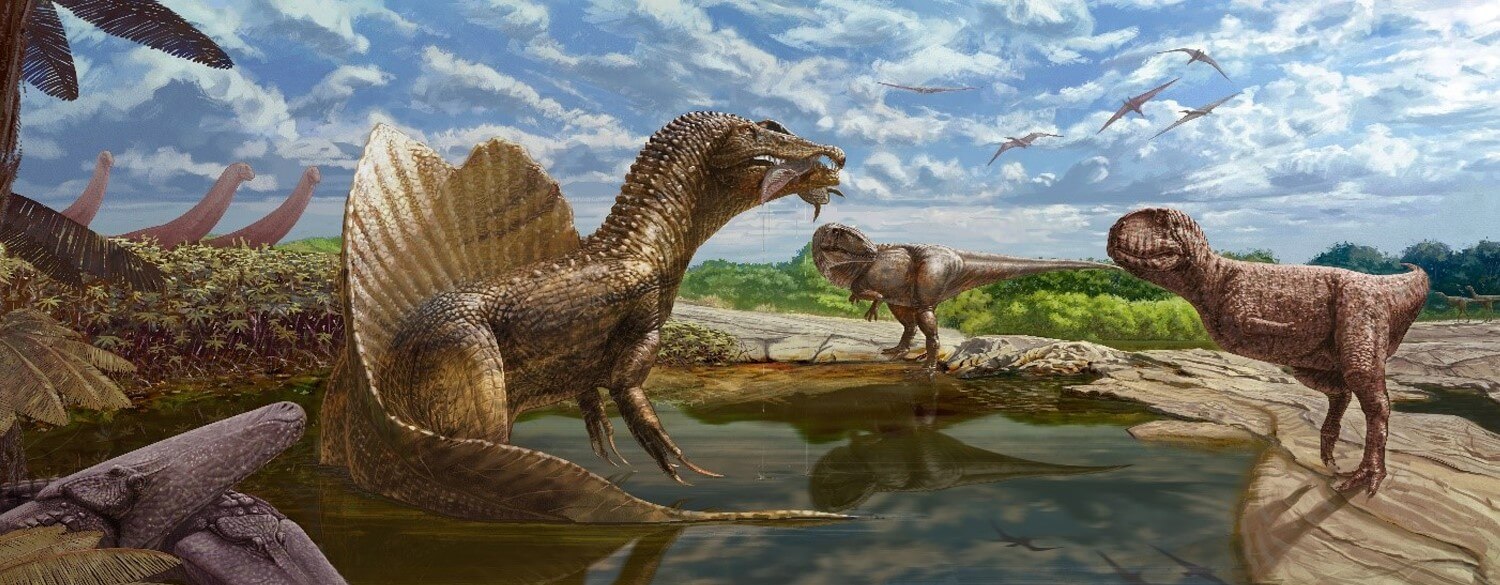
Spinosaurus: This semi-aquatic predator focused on fish, with conical teeth perfect for gripping slippery prey.
Ankylosaurus: With its low-slung body and armored exterior, Ankylosaurus grazed on ground-level vegetation, relying on its strong jaws to crush tough plants.
Dietary specialization often shaped a dinosaur’s niche but could make them vulnerable to environmental changes.
Impact of Diets on Ecosystems
 Dinosaur diets played a crucial role in shaping their ecosystems:
Dinosaur diets played a crucial role in shaping their ecosystems:
Herbivores helped maintain plant diversity by consuming vegetation and spreading seeds.
Carnivores controlled herbivore populations, preventing overgrazing.
Omnivores filled gaps, maintaining ecological balance.
FAQs
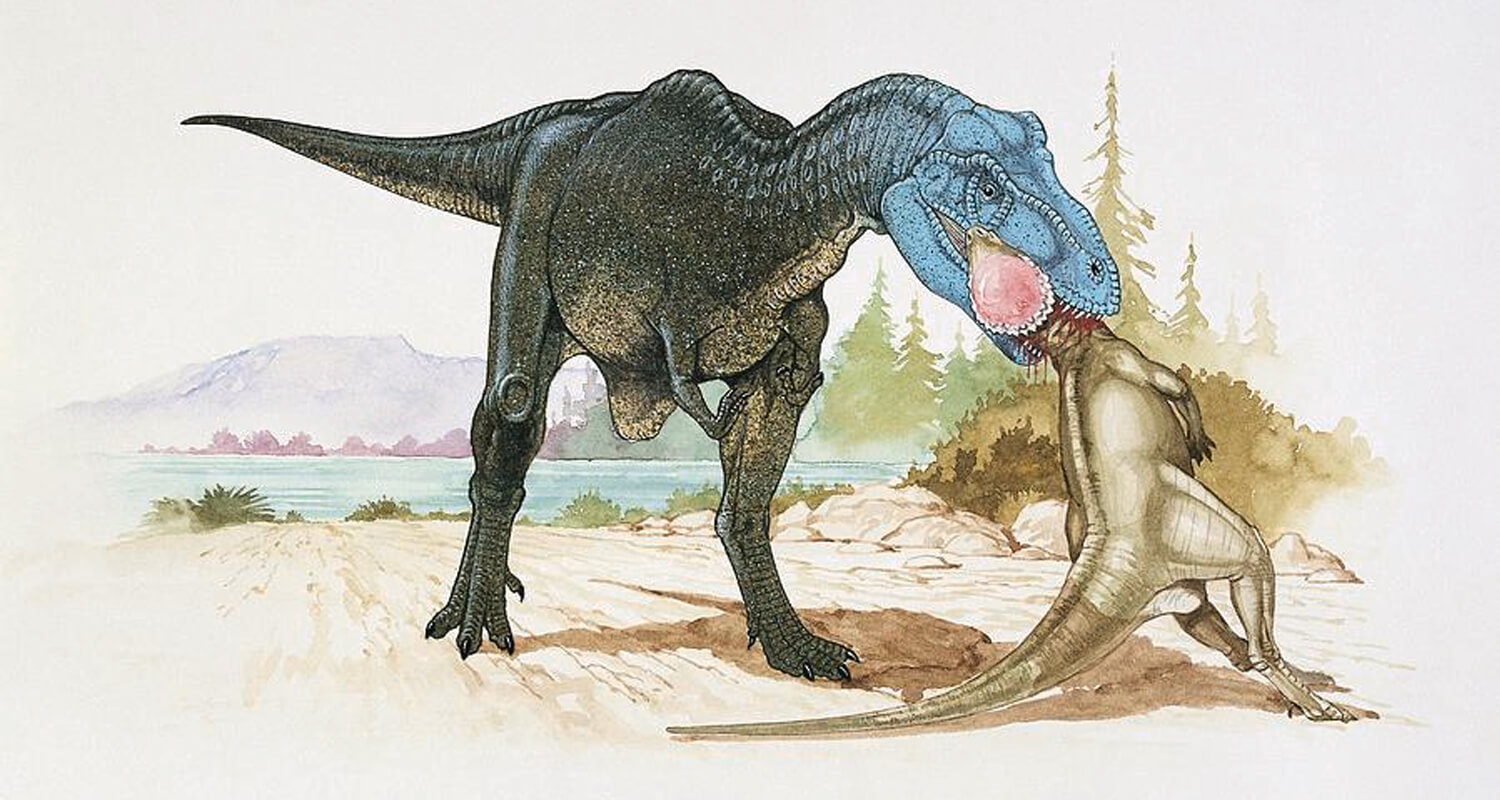 What did the largest dinosaurs eat?
What did the largest dinosaurs eat?
The largest dinosaurs, such as Brachiosaurus and Argentinosaurus, were herbivores that fed on trees, ferns, and other vegetation.
Did all dinosaurs eat meat or plants?
No, some dinosaurs were omnivores, eating both plants and small animals.
How do we know what dinosaurs ate if they lived millions of years ago?
Paleontologists study teeth, coprolites, and other fossil evidence to determine dietary habits.
Were there dinosaurs that ate insects or fish?
Yes, dinosaurs like Spinosaurus specialized in eating fish, and smaller dinosaurs may have fed on insects.
Conclusion
 Dinosaurs exhibited incredible dietary diversity, from towering herbivores to agile carnivores and adaptable omnivores. Their diets shaped ancient ecosystems, influencing plant growth and animal populations. By studying what dinosaurs ate, we uncover fascinating details about their behavior, survival strategies, and the world they lived in.
Dinosaurs exhibited incredible dietary diversity, from towering herbivores to agile carnivores and adaptable omnivores. Their diets shaped ancient ecosystems, influencing plant growth and animal populations. By studying what dinosaurs ate, we uncover fascinating details about their behavior, survival strategies, and the world they lived in.
Want to see dinosaurs'diets in action? Explore our animatronic dinosaur models for an unforgettable prehistoric experience!












