Pteranodon vs. Pterodactyl: Decoding the Differences of Ancient Flyers
Date:2024/08/28 Visits:5415
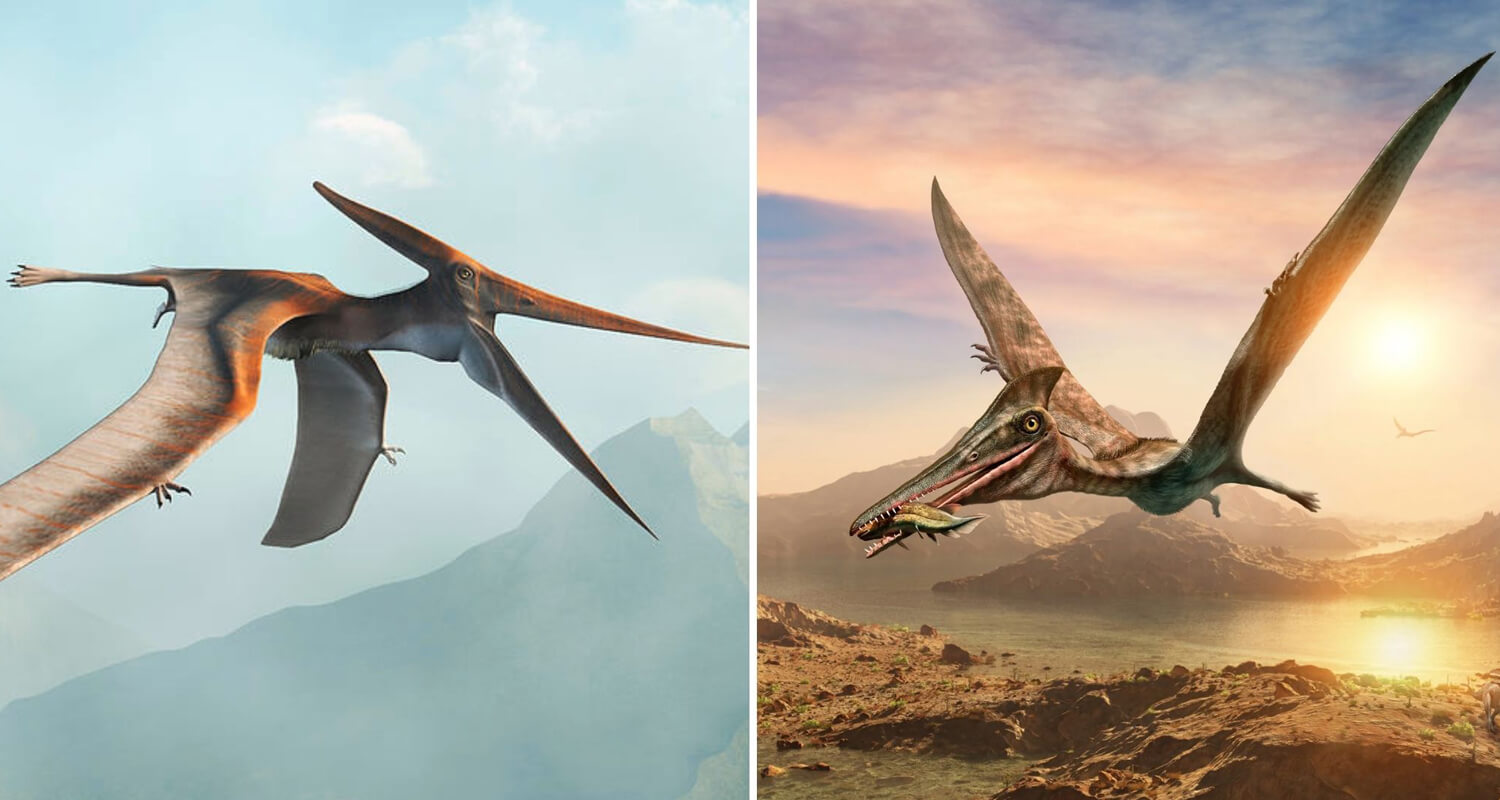 In the captivating world of prehistoric flying reptiles, the Pteranodon and the Pterodactyl are often discussed and sometimes confused. Both belong to the larger group of pterosaurs but exhibit distinct features and lived in different periods. In this article, we will delve into the differences and similarities between these two fascinating creatures and explore how our animatronic dinosaurs can bring their ancient majesty to life.
In the captivating world of prehistoric flying reptiles, the Pteranodon and the Pterodactyl are often discussed and sometimes confused. Both belong to the larger group of pterosaurs but exhibit distinct features and lived in different periods. In this article, we will delve into the differences and similarities between these two fascinating creatures and explore how our animatronic dinosaurs can bring their ancient majesty to life.
Pteranodon: The Great Sky Navigator
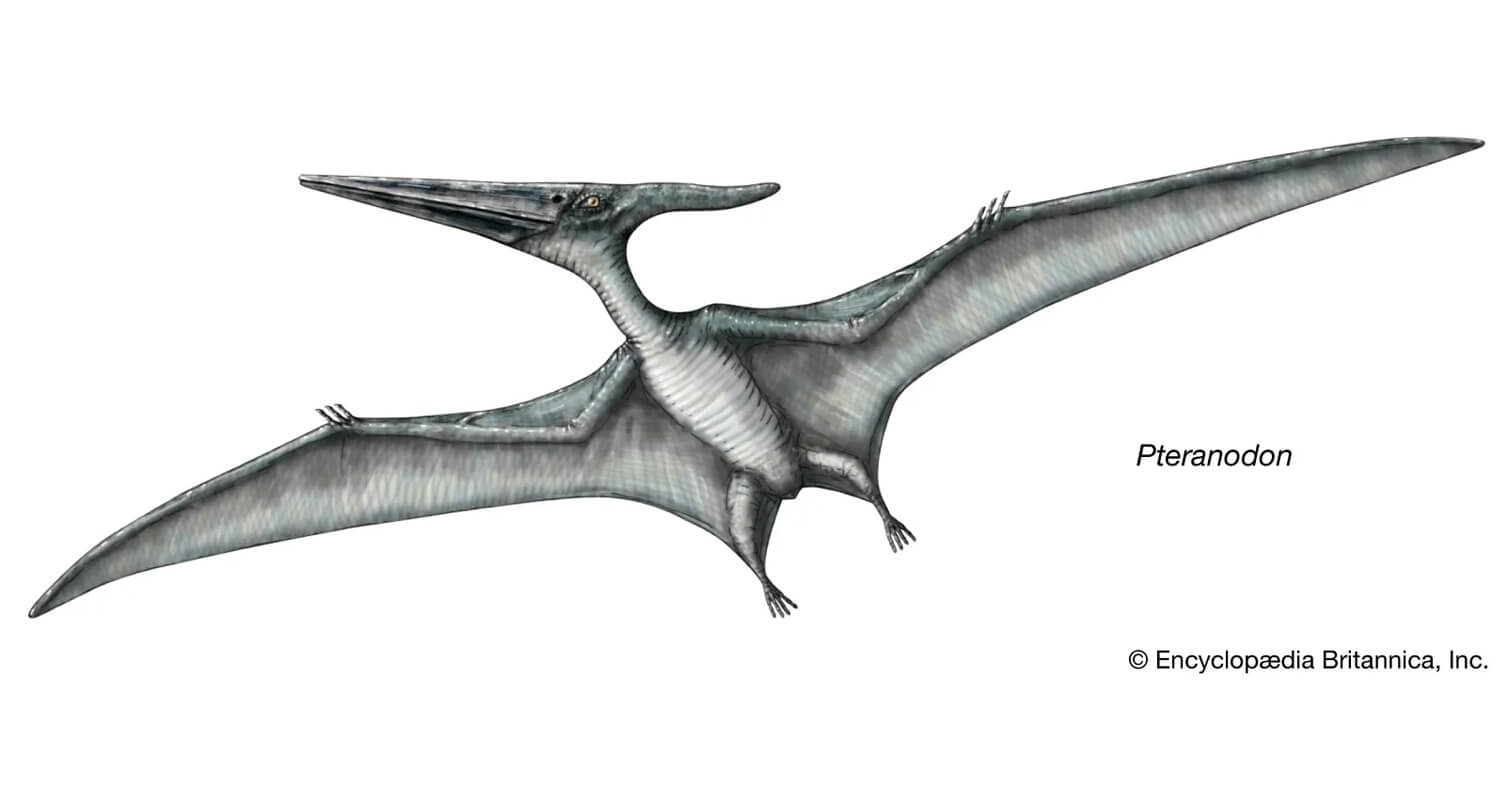 The Pteranodon, which translates to "toothless wing," soared through the skies during the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 70 to 100 million years ago. This genus of pterosaur is notable for several key characteristics:
The Pteranodon, which translates to "toothless wing," soared through the skies during the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 70 to 100 million years ago. This genus of pterosaur is notable for several key characteristics:
Impressive Wingspan: Pteranodons are famous for their enormous wingspan, which could reach up to 33 feet in some species. This made them some of the largest flying reptiles, well-adapted to soaring long distances.
Distinctive Cranial Crest: One of the most striking features of the Pteranodon is its large, often elaborate cranial crest. The shape and size of this crest varied between species and likely played a role in sexual display or aerodynamic efficiency.
Diet and Feeding Habits: With a toothless beak, the Pteranodon primarily fed on fish, which it likely caught while gliding over bodies of water. Its adaptation for a piscivorous diet is evident in its streamlined body and large wings.
Pterodactyl: The Agile Flyer
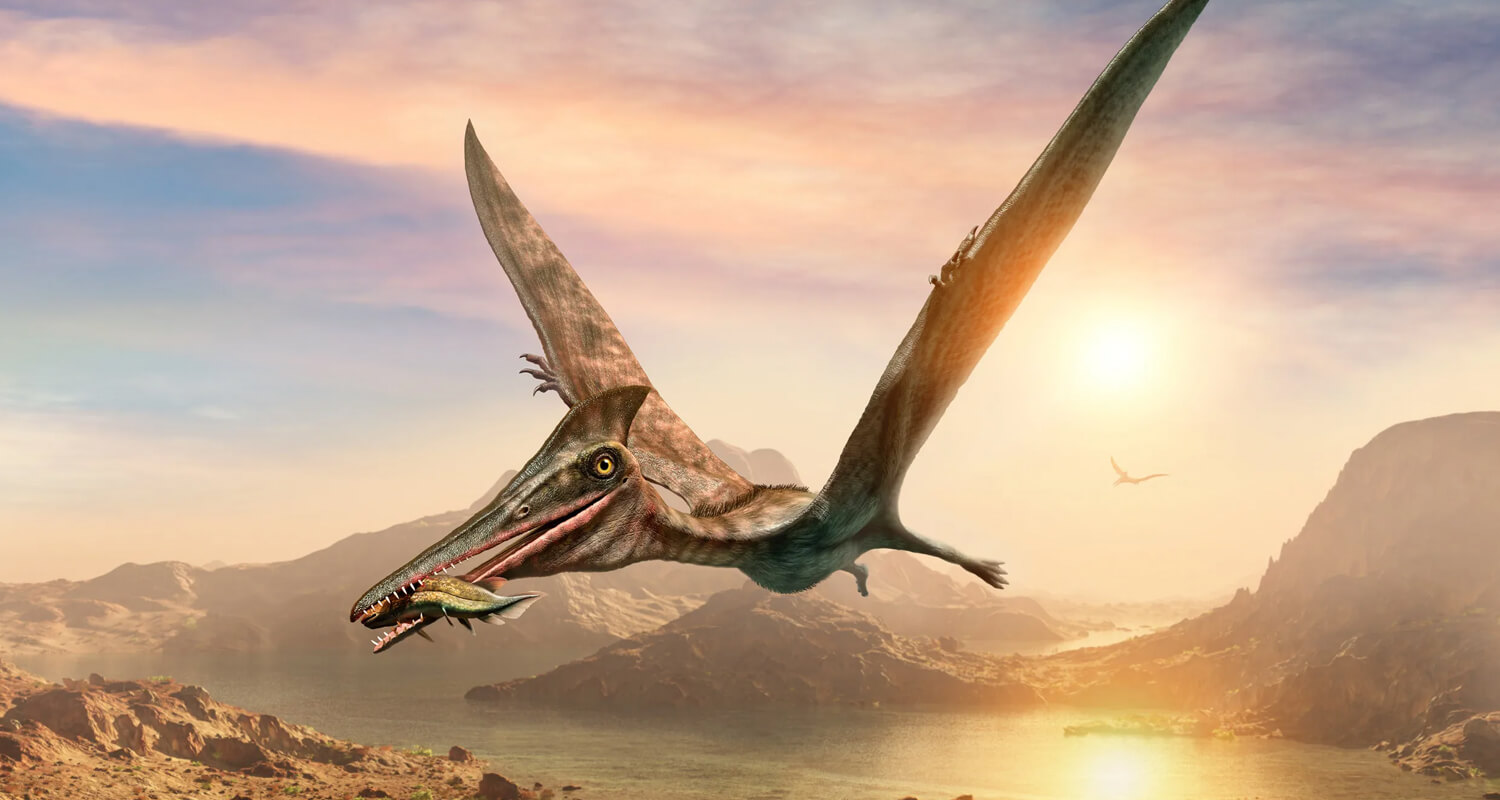 The term "Pterodactyl" often refers to various pterosaurs, but specifically, it denotes members of the genus Pterodactylus, which lived during the Late Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. Key features of Pterodactylus include:
The term "Pterodactyl" often refers to various pterosaurs, but specifically, it denotes members of the genus Pterodactylus, which lived during the Late Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. Key features of Pterodactylus include:
Smaller Wingspan: Unlike the Pteranodon, Pterodactylus had a more modest wingspan, ranging from 3 to 10 feet. This smaller size made it more agile and suited for quick, maneuverable flight.
Pronounced Beak: Pterodactylus had a more pronounced, hooked beak compared to the Pteranodon, indicating a diet that might have included insects or small vertebrates.
Body Structure: The body of Pterodactylus was more compact and less specialized for long-distance flight, reflecting its adaptation to different ecological niches compared to the larger Pteranodon.
Pteranodon vs. Pterodactyl: Key Differences

Wingspan and Flight Capabilities: Pteranodons had a much larger wingspan than Pterodactylus, which allowed them to glide over vast distances. Pterodactylus, with its smaller wings, was better suited for agile, short-distance flights.
Cranial Features: The Pteranodon’s large cranial crest was a notable feature not present in Pterodactylus. This crest may have had both display and aerodynamic functions. Pterodactylus lacked such a prominent crest, reflecting different ecological and evolutionary pressures.
Diet and Feeding Strategies: The toothless beak of the Pteranodon indicates a diet focused on fish, while the hooked beak of Pterodactylus suggests a more varied diet that could include smaller prey.
Bringing Prehistoric Flyers to Life with Animatronic Dinosaurs
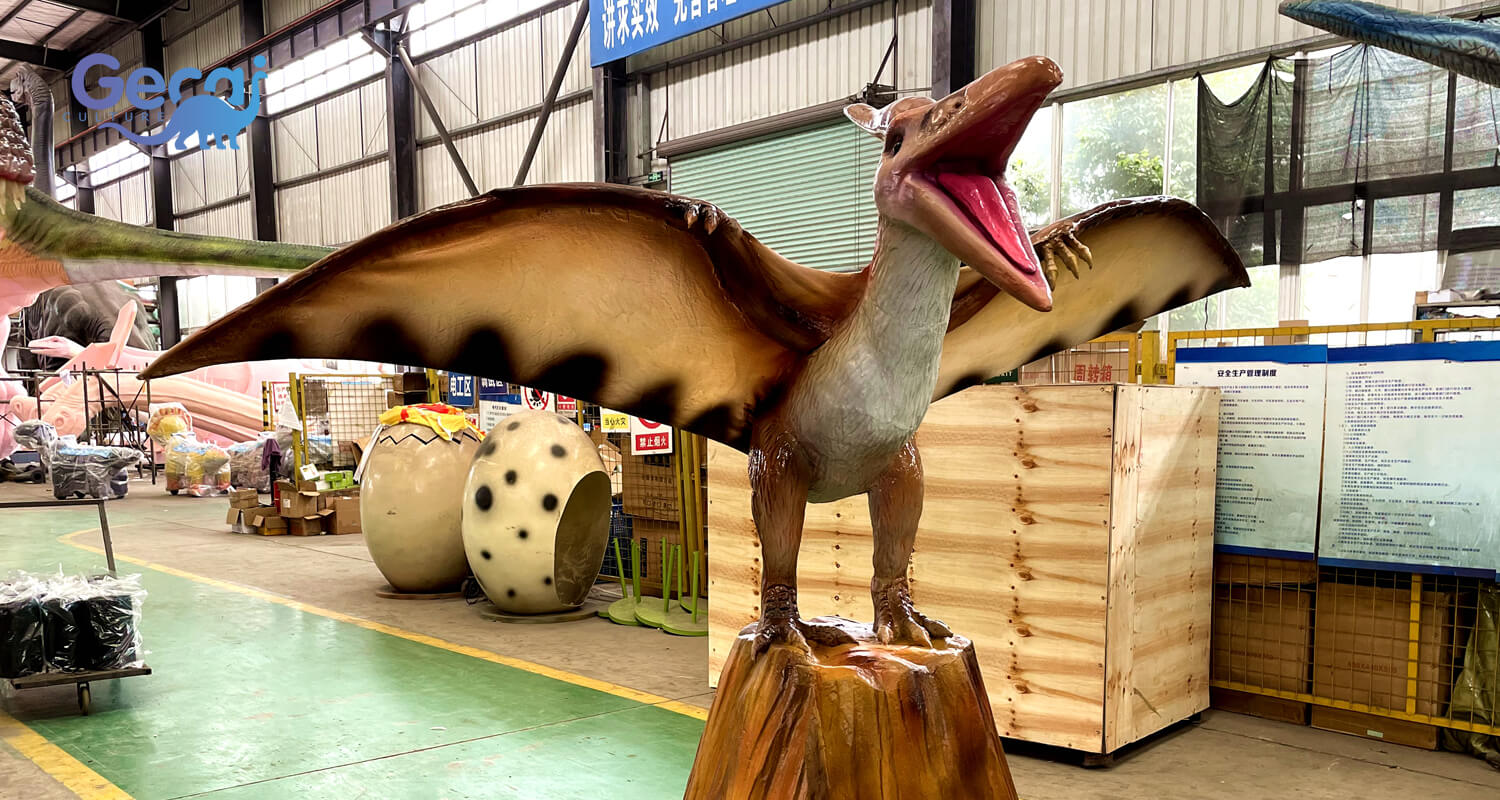 For those eager to experience the grandeur of these ancient flying reptiles, consider integrating our animatronic dinosaurs into your displays. Our Pteranodon and Pterodactyl animatronics are crafted with attention to detail, replicating the size, movement, and appearance of these prehistoric flyers. These lifelike models offer an engaging and educational way to explore the differences and similarities between these remarkable creatures. Ideal for museums, theme parks, and educational events, our animatronic dinosaurs bring a touch of the Mesozoic era to life.
For those eager to experience the grandeur of these ancient flying reptiles, consider integrating our animatronic dinosaurs into your displays. Our Pteranodon and Pterodactyl animatronics are crafted with attention to detail, replicating the size, movement, and appearance of these prehistoric flyers. These lifelike models offer an engaging and educational way to explore the differences and similarities between these remarkable creatures. Ideal for museums, theme parks, and educational events, our animatronic dinosaurs bring a touch of the Mesozoic era to life.
FAQs about Pteranodon and Pterodactyl
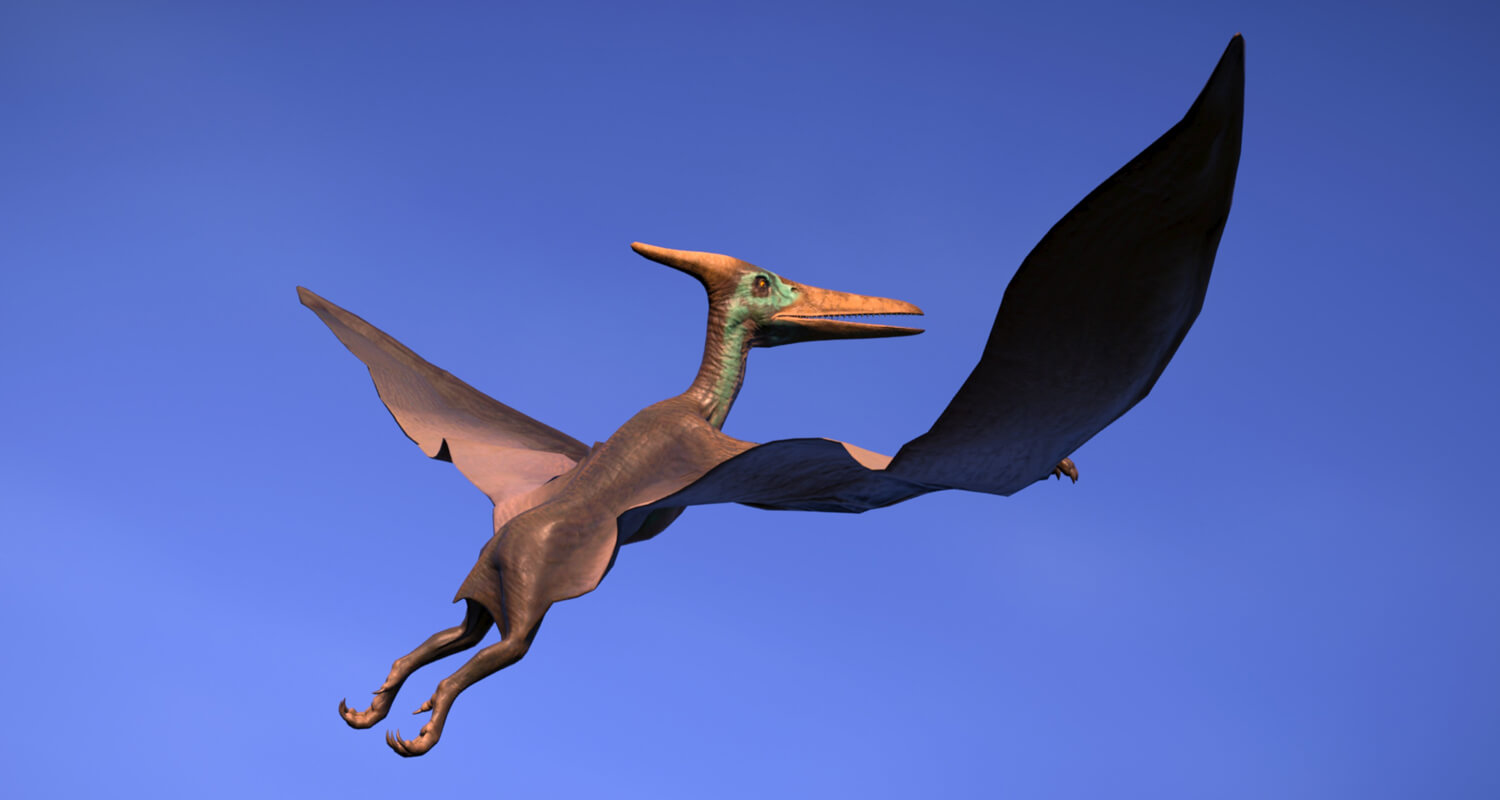 What are the main differences between Pteranodon and Pterodactylus?
What are the main differences between Pteranodon and Pterodactylus?
The primary differences include wingspan size, with Pteranodon having a much larger wingspan suitable for long-distance flight and Pterodactylus being more agile with a smaller wingspan. Additionally, Pteranodon had a prominent cranial crest, while Pterodactylus did not.
Which of these pterosaurs was larger?
Pteranodon was generally larger, with a wingspan reaching up to 33 feet, compared to Pterodactylus's wingspan of 3 to 10 feet.
Did Pterodactylus have any special adaptations?
Yes, Pterodactylus had a hooked beak suitable for feeding on a variety of smaller prey, and its smaller size made it more agile in flight.
Conclusion
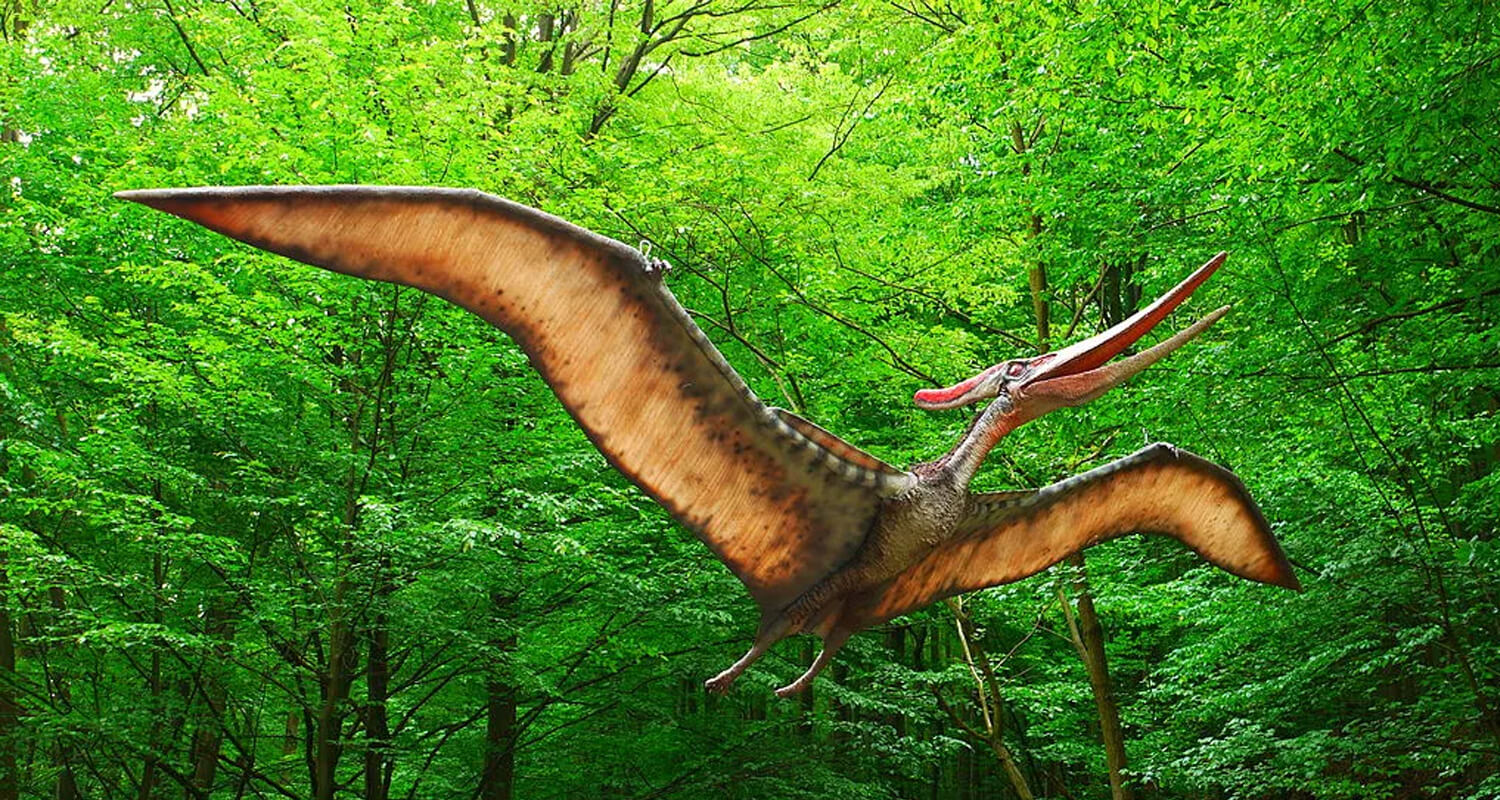 Pteranodon and Pterodactylus, while both fascinating flying reptiles, highlight the diversity and specialization within the pterosaur group. By understanding their differences and unique traits, we gain valuable insights into their respective roles in prehistoric ecosystems. Our animatronic Pteranodon and Pterodactylus models offer an exciting way to bring these ancient flyers to life, making them perfect for educational and entertaining purposes. Whether for a museum exhibit or a themed event, our animatronics provide an engaging way to explore the incredible world of prehistoric aviation.
Pteranodon and Pterodactylus, while both fascinating flying reptiles, highlight the diversity and specialization within the pterosaur group. By understanding their differences and unique traits, we gain valuable insights into their respective roles in prehistoric ecosystems. Our animatronic Pteranodon and Pterodactylus models offer an exciting way to bring these ancient flyers to life, making them perfect for educational and entertaining purposes. Whether for a museum exhibit or a themed event, our animatronics provide an engaging way to explore the incredible world of prehistoric aviation.












