Carnivores vs. Herbivores: The Great Dinosaur Rivalry
Date:2024/12/10 Visits:2622
 Dinosaurs ruled the Earth during the Mesozoic era, leaving a legacy that continues to captivate scientists and enthusiasts alike. Among these ancient giants, the dynamic between carnivorous and herbivorous dinosaurs stands out as a testament to the power of evolution and survival. This epic rivalry shaped ecosystems and inspired a wealth of theories about life millions of years ago. Let's dive into the details of this great dinosaur struggle.
Dinosaurs ruled the Earth during the Mesozoic era, leaving a legacy that continues to captivate scientists and enthusiasts alike. Among these ancient giants, the dynamic between carnivorous and herbivorous dinosaurs stands out as a testament to the power of evolution and survival. This epic rivalry shaped ecosystems and inspired a wealth of theories about life millions of years ago. Let's dive into the details of this great dinosaur struggle.
Understanding Carnivorous Dinosaurs
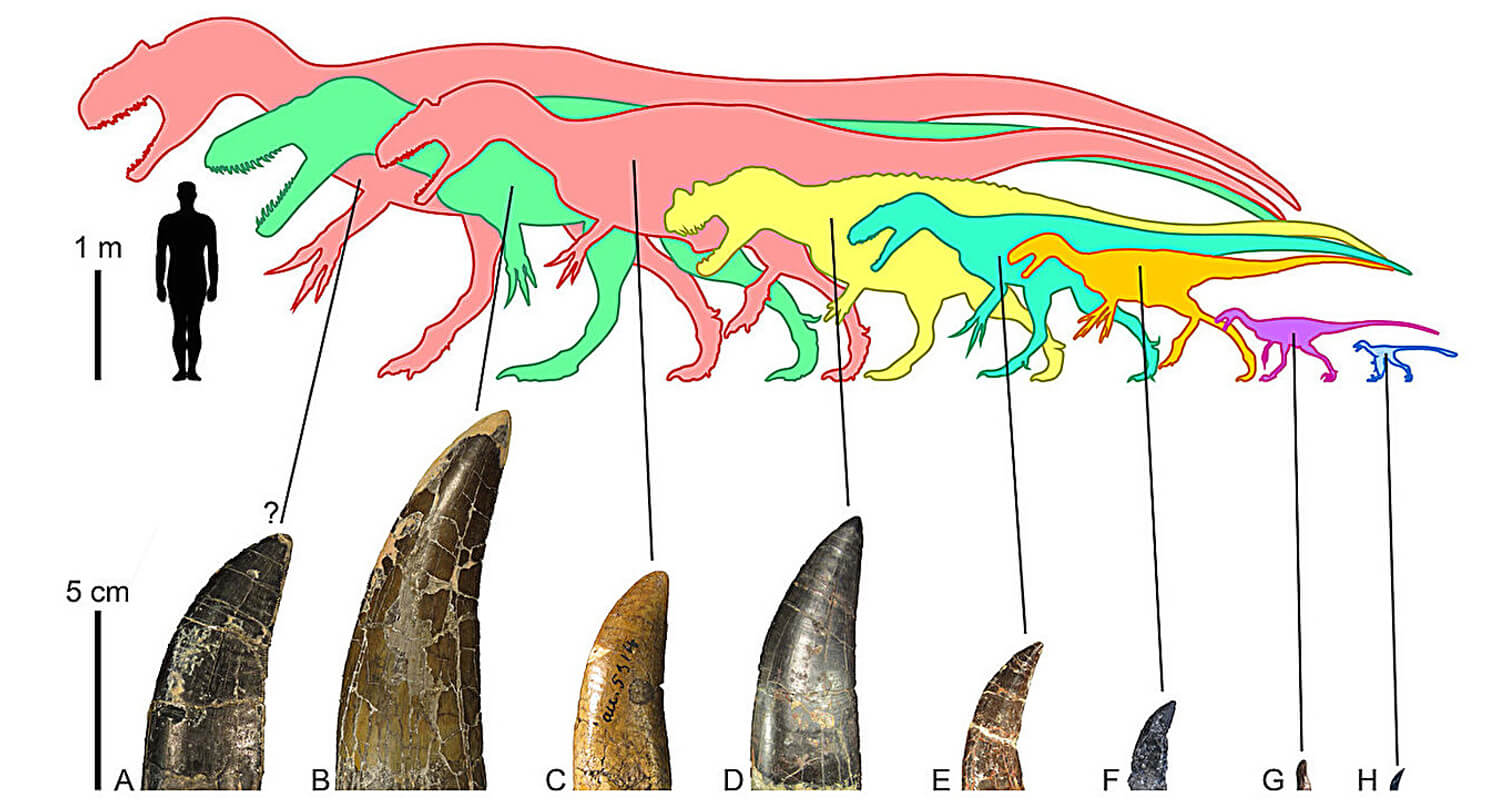 Carnivorous dinosaurs were apex predators, evolving adaptations to dominate the food chain. Equipped with sharp teeth, powerful jaws, and razor-like claws, they were designed to hunt. Many were bipedal, allowing for agility and speed in chasing prey.
Carnivorous dinosaurs were apex predators, evolving adaptations to dominate the food chain. Equipped with sharp teeth, powerful jaws, and razor-like claws, they were designed to hunt. Many were bipedal, allowing for agility and speed in chasing prey.
Prominent examples include Tyrannosaurus rex, known for its immense size and crushing bite force; Velociraptor, a smaller but highly intelligent predator; and Giganotosaurus, one of the largest carnivores ever to walk the Earth.
These predators played a vital role in maintaining balance in their ecosystems by regulating prey populations. Some also scavenged, making use of carcasses to sustain themselves, which further emphasized their importance in prehistoric environments.
Understanding Herbivorous Dinosaurs
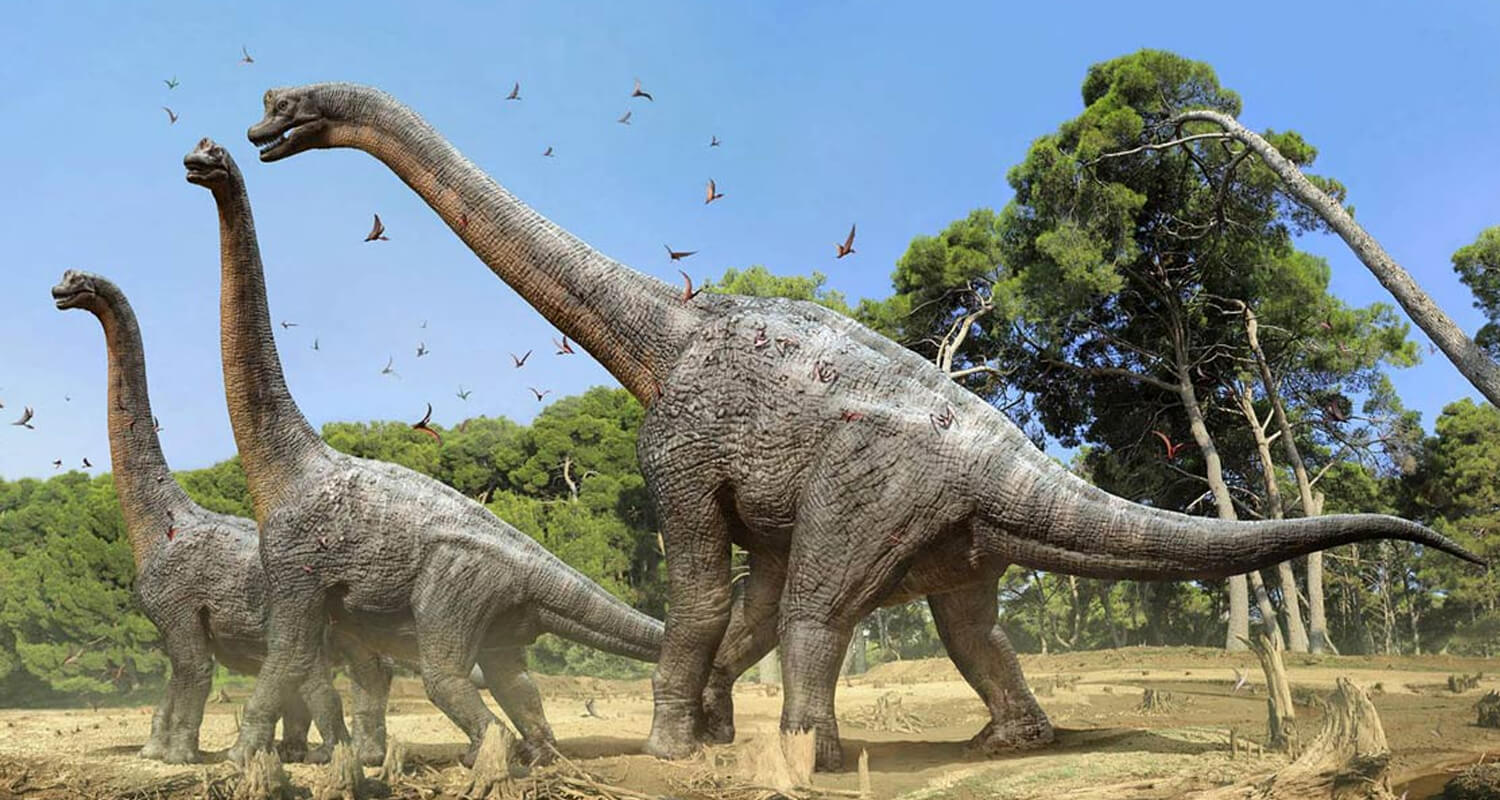 Herbivorous dinosaurs were the plant-eating giants that sustained the food chain's base. With specialized flat teeth and efficient digestive systems, they could process tough vegetation. To protect themselves from predators, herbivores evolved remarkable defenses, including spikes, armored plates, and sheer size.
Herbivorous dinosaurs were the plant-eating giants that sustained the food chain's base. With specialized flat teeth and efficient digestive systems, they could process tough vegetation. To protect themselves from predators, herbivores evolved remarkable defenses, including spikes, armored plates, and sheer size.
Key examples include Triceratops, with its formidable horns and shield-like frill; Brachiosaurus, towering above predators at great heights; and Stegosaurus, whose tail spikes were a lethal weapon against attackers.
Their primary role in the ecosystem was consuming vegetation, controlling plant overgrowth, and dispersing seeds. Without herbivores, the lush prehistoric landscapes would have been unmanageable, disrupting the balance for all life forms.
The Great Rivalry
Predator-Prey Dynamics
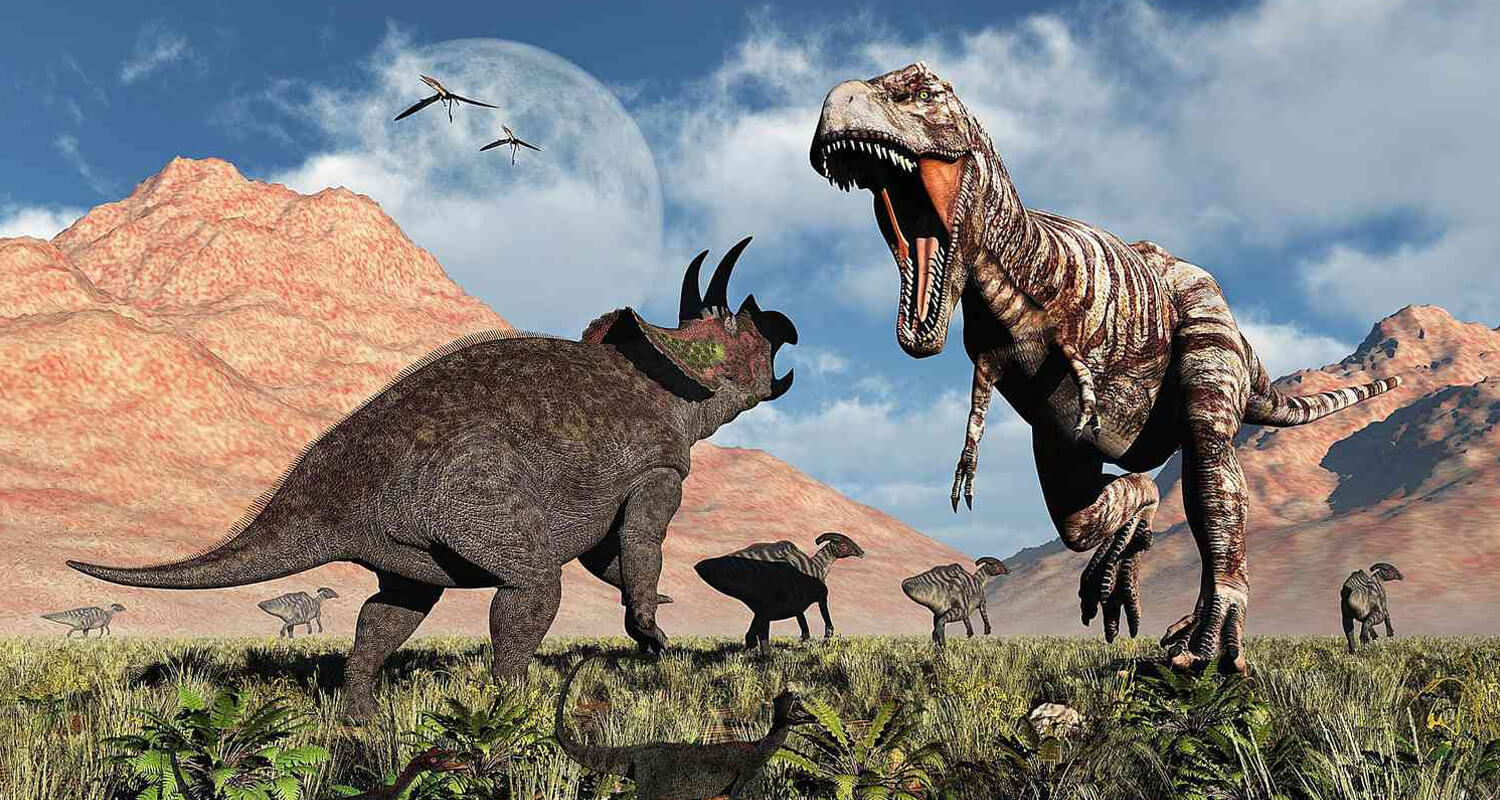 The carnivore-herbivore relationship revolved around survival. Carnivores relied on stealth, speed, and strategic attacks, often hunting in packs or ambushing their prey. Herbivores, on the other hand, defended themselves through size, physical adaptations, and group behaviors like herding.
The carnivore-herbivore relationship revolved around survival. Carnivores relied on stealth, speed, and strategic attacks, often hunting in packs or ambushing their prey. Herbivores, on the other hand, defended themselves through size, physical adaptations, and group behaviors like herding.
Iconic Showdowns
One of the most discussed rivalries is Tyrannosaurus rex vs. Triceratops, which fossil evidence suggests may have clashed in life. The T. rex's powerful bite met its match in Triceratops' defensive horns and frill. Such confrontations highlight the tension between predator and prey, showcasing nature's unforgiving cycle of survival.
Evolutionary Arms Race
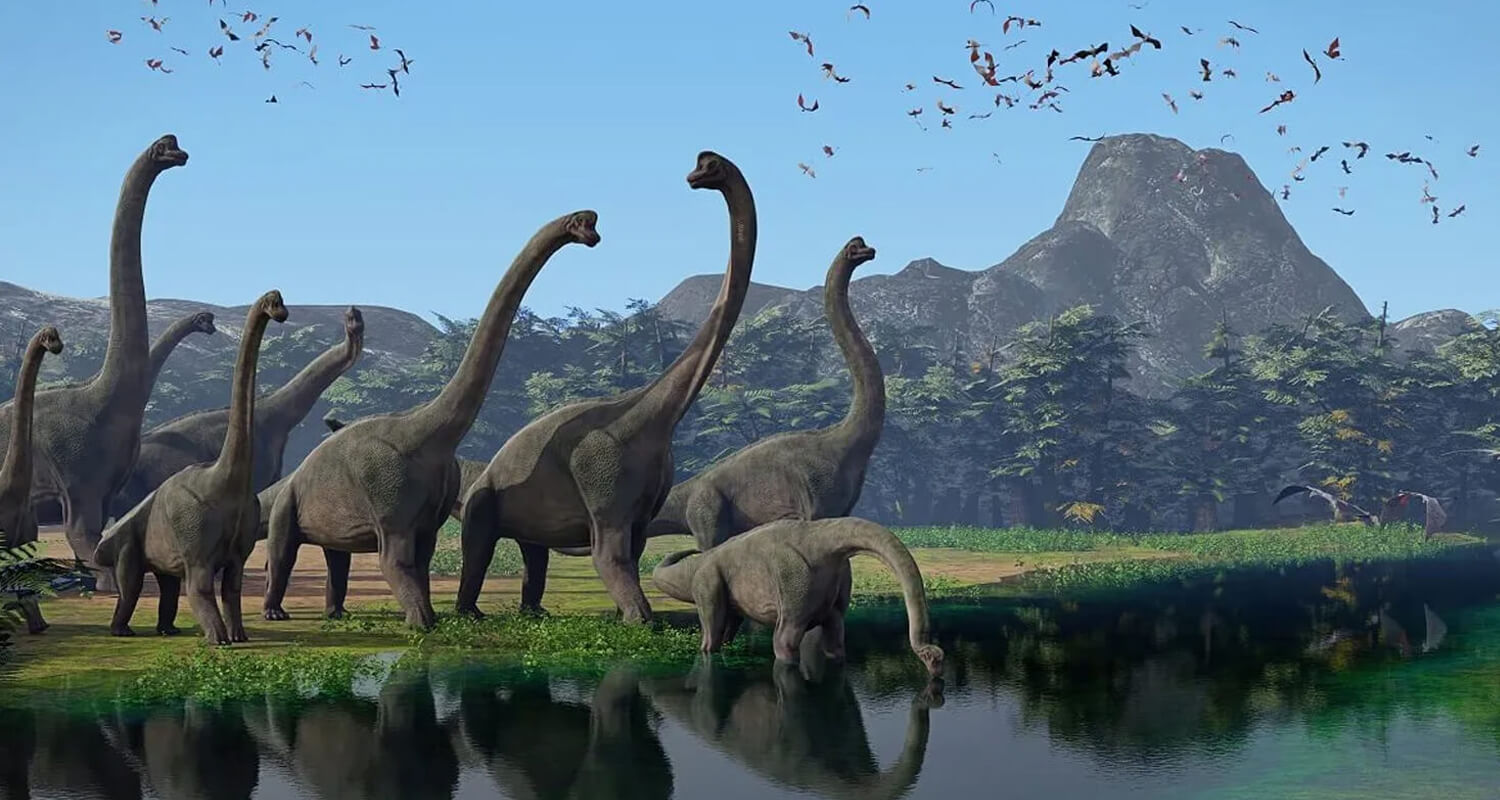 The rivalry between carnivores and herbivores spurred an evolutionary arms race. As carnivores developed sharper claws, stronger jaws, and enhanced intelligence, herbivores countered with larger sizes, tougher armor, and advanced defensive strategies.
The rivalry between carnivores and herbivores spurred an evolutionary arms race. As carnivores developed sharper claws, stronger jaws, and enhanced intelligence, herbivores countered with larger sizes, tougher armor, and advanced defensive strategies.
This constant competition drove the diversification of species, leading to some of the most incredible adaptations seen in the fossil record. It's a testament to how rivalry and survival pressures shape life on Earth.
Lessons from the Rivalry
The carnivore-herbivore dynamic offers insights into the delicate balance of ecosystems. It highlights how competition can drive evolutionary innovation, ensuring biodiversity thrives. Moreover, this prehistoric struggle mirrors similar dynamics seen in modern ecosystems, offering a glimpse into the interconnectedness of life.
FAQs
 Why were carnivorous dinosaurs often smaller than herbivores?
Why were carnivorous dinosaurs often smaller than herbivores?
Carnivores needed speed and agility to hunt, while herbivores relied on size for defense. This difference shaped their physical attributes.
Did carnivorous dinosaurs only eat meat?
While most were strict meat-eaters, some carnivores, like certain raptors, may have scavenged or eaten eggs and smaller prey.
How did herbivores defend themselves from predators?
Herbivores used physical features like horns, tail spikes, or thick armor, as well as herding behavior to deter predators.
Which group was more dominant during the dinosaur era?
Neither group was universally dominant; their coexistence and interdependence maintained ecosystem balance.
Conclusion
 The rivalry between carnivorous and herbivorous dinosaurs defined the Mesozoic era, driving evolution and shaping ecosystems. From thrilling hunts to incredible defensive adaptations, these interactions continue to captivate our imaginations. Through animatronic recreations, we can relive these prehistoric battles, bringing the ancient world back to life for everyone to enjoy.
The rivalry between carnivorous and herbivorous dinosaurs defined the Mesozoic era, driving evolution and shaping ecosystems. From thrilling hunts to incredible defensive adaptations, these interactions continue to captivate our imaginations. Through animatronic recreations, we can relive these prehistoric battles, bringing the ancient world back to life for everyone to enjoy.












