What Killed the Dinosaurs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Extinction
Date:2024/07/08 Visits:156
The extinction of dinosaurs, an event shrouded in mystery and fascination, has captivated scientists and enthusiasts alike for centuries. Numerous theories have been proposed to explain this cataclysmic event, ranging from celestial catastrophes to terrestrial upheavals. This article delves into the leading theories and explores the factors that may have led to the demise of these magnificent creatures.
Exploding Star

One of the more unconventional theories suggests that a nearby supernova, an exploding star, could have bombarded Earth with harmful radiation. This radiation, in turn, may have disrupted the climate and ecosystems, contributing to the decline of dinosaurs.
Meteor Impact
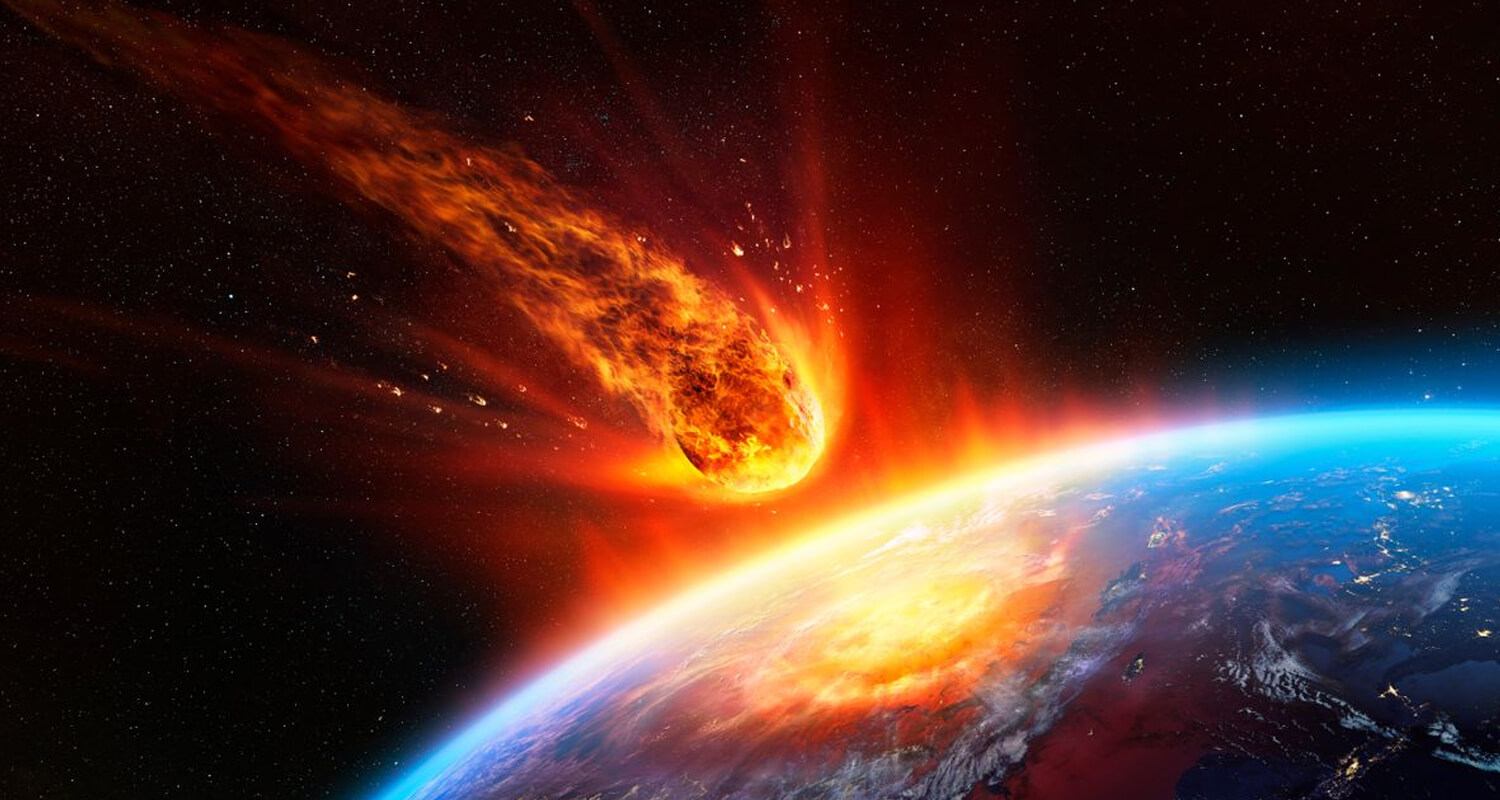

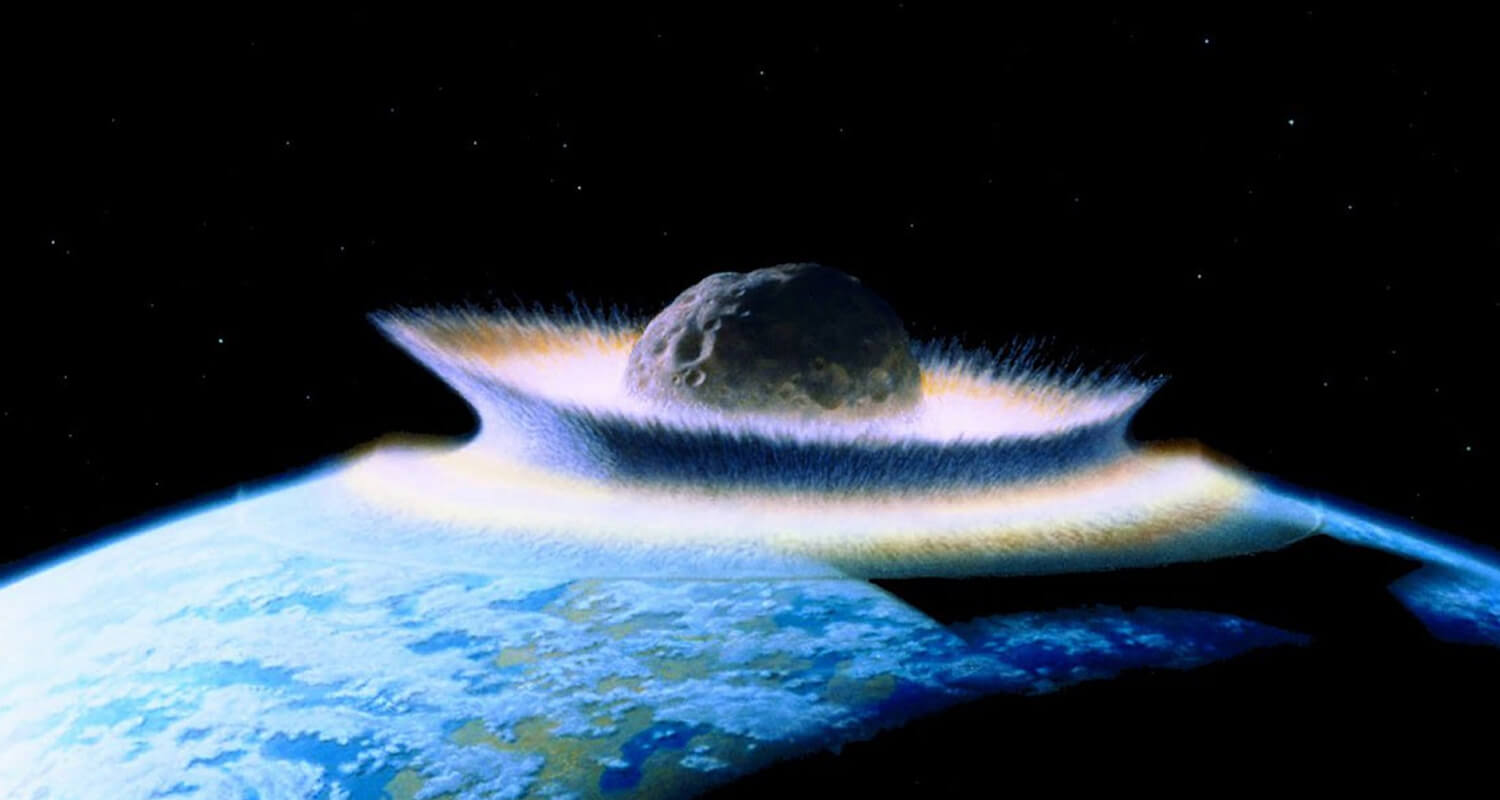
Perhaps the most widely accepted theory is the impact of a massive meteor or asteroid around 66 million years ago. This impact, known as the Chicxulub crater in modern-day Mexico, unleashed global devastation. The ensuing dust and debris clouded the atmosphere, blocking sunlight and triggering a dramatic drop in temperatures—a phenomenon known as an impact winter.
Unbearable Heat and Darkness

Conversely, volcanic activity could have unleashed immense amounts of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere. This scenario would have intensified the greenhouse effect, leading to scorching temperatures that many species, including dinosaurs, could not endure.
Following the meteor impact or volcanic eruptions, a period of darkness—sometimes lasting months—may have enveloped the planet. Without sunlight, photosynthesis would have faltered, disrupting food chains and causing widespread ecological collapse.
Volcanic Eruptions
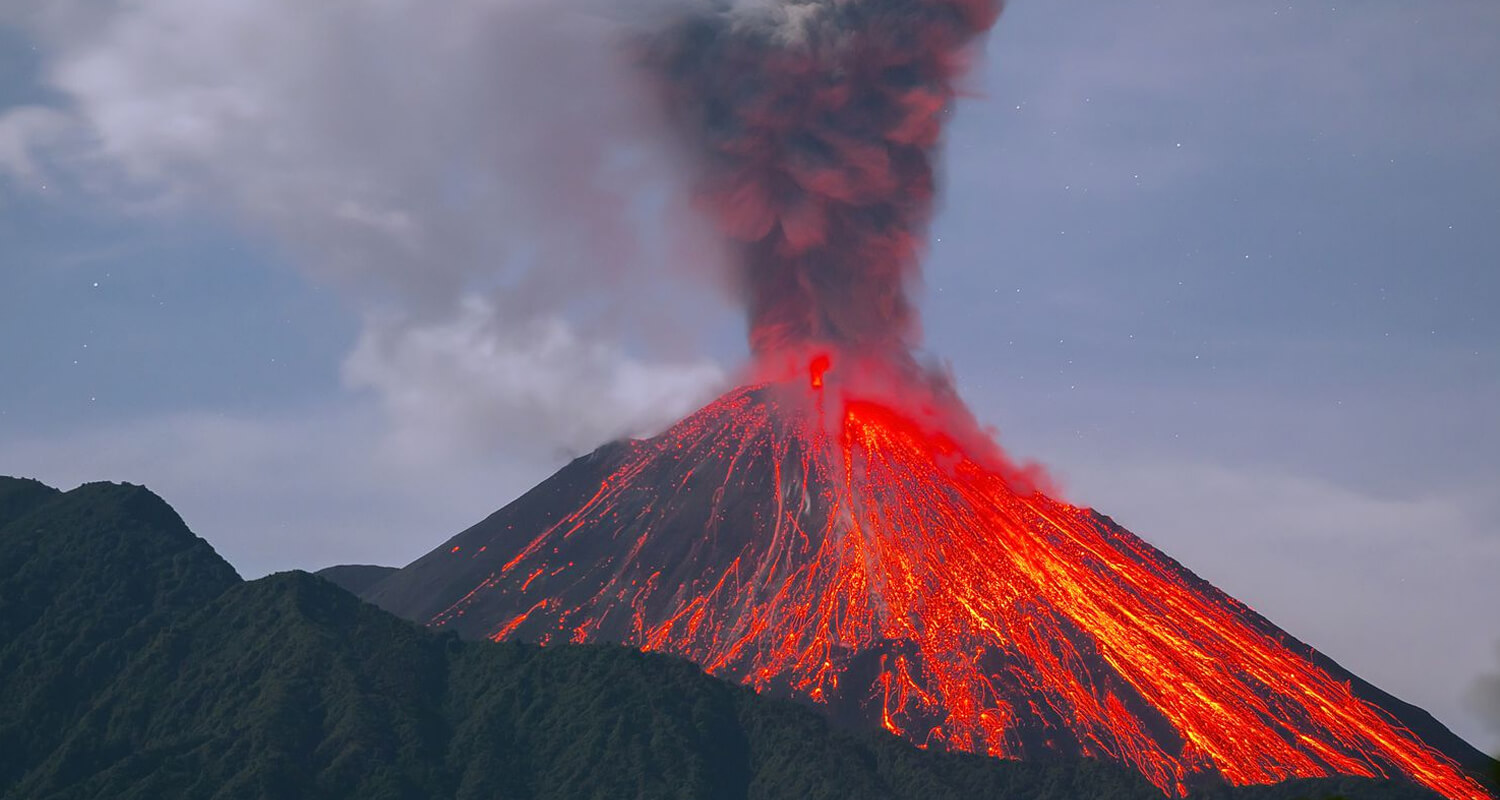

Volcanic eruptions, such as those in the Deccan Traps of present-day India, occurred around the time of the dinosaur extinction. These eruptions released vast amounts of lava and gases, further altering Earth's climate and contributing to the environmental stress faced by dinosaurs.
Combination of These Events
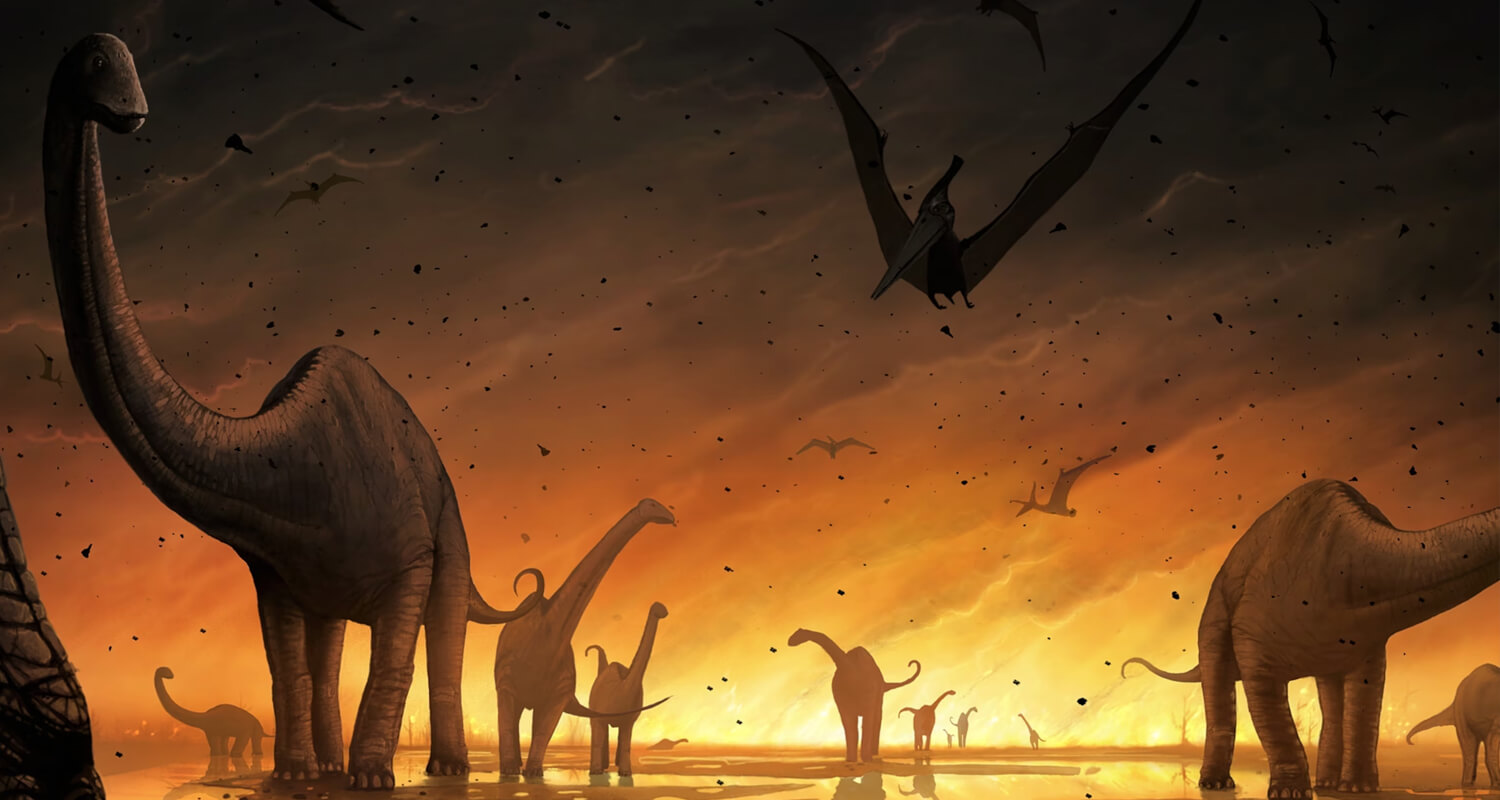

Ultimately, it is likely that a combination of these factors—meteor impact, volcanic eruptions, climate change, and environmental disruptions—contributed to the extinction of dinosaurs. This cataclysmic chain of events reshaped Earth's ecosystems and paved the way for the rise of mammals and eventually, humans.
Frequently Asked Questions
 When did dinosaurs go extinct?
When did dinosaurs go extinct?
Dinosaurs went extinct around 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event.
Did humans exist with dinosaurs?
No, dinosaurs went extinct millions of years before the first humans appeared on Earth.
Did any dinosaurs survive?
Some descendants of dinosaurs, such as birds, survived the extinction event and continue to thrive today.
Conclusion
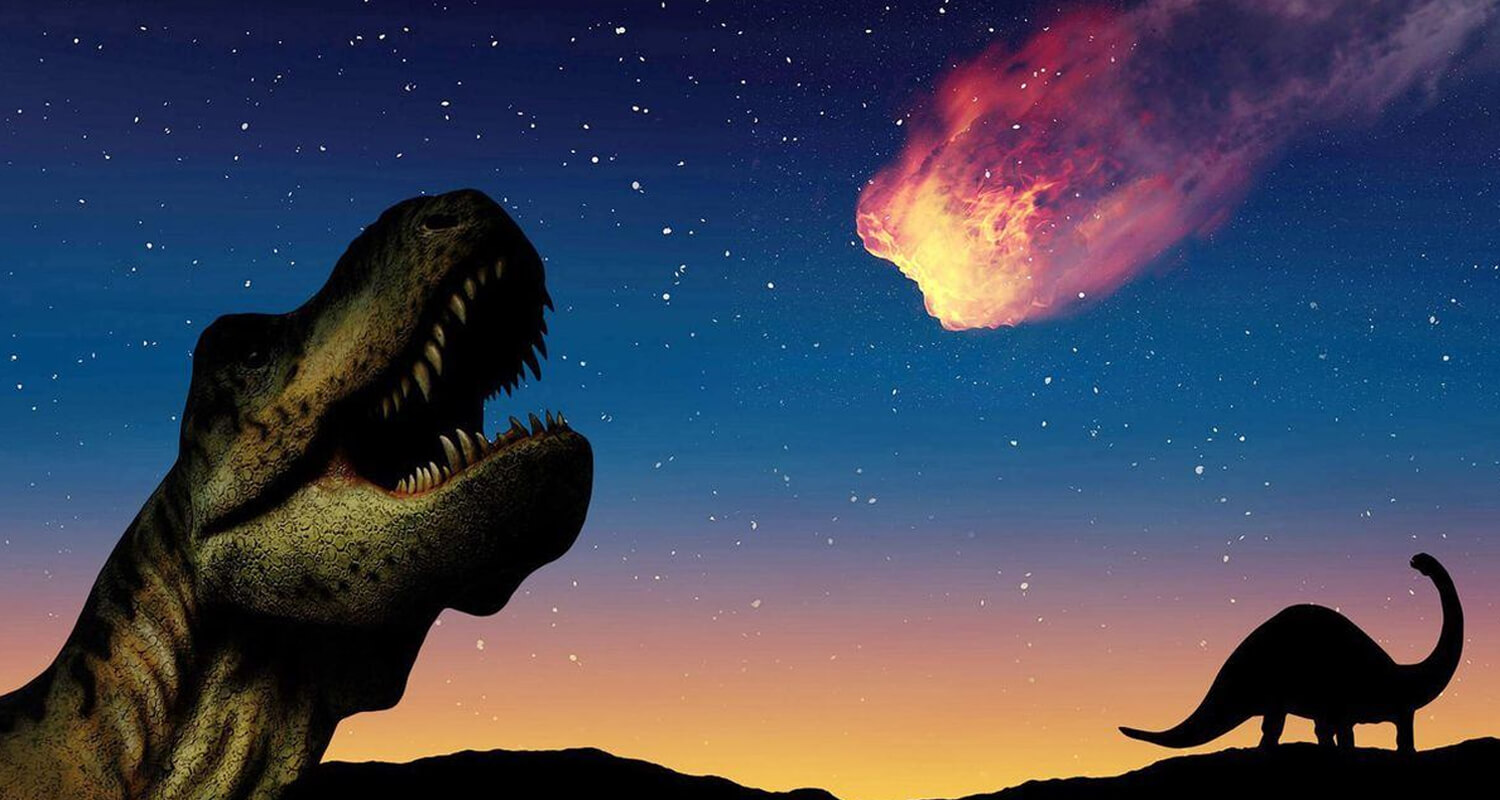

The extinction of dinosaurs remains a poignant reminder of Earth's ever-changing landscape and the delicate balance of life on our planet. While many questions still linger, ongoing research continues to shed light on the events that shaped our world and paved the way for new forms of life to emerge.
By exploring these theories and answering common questions, we gain a deeper understanding of what killed the dinosaurs and the profound impact it had on the course of natural history.
While the physical dinosaurs vanished millions of years ago, their legacy lives on through innovative recreations like animatronic dinosaurs. These lifelike models, such as those crafted by us, allow audiences to experience the awe-inspiring presence of dinosaurs firsthand. With customizable features and realistic movements, these animatronic dinosaurs bring the ancient world into the modern era, captivating audiences in museums, theme parks, and exhibitions worldwide.