Dinosaurs and the Weather: How Climate Change Affected Their Evolution
Date:2025/02/06 Visits:202
 Dinosaurs ruled the Earth for over 160 million years, adapting to various environmental changes. However, the climate played a significant role in their evolution, shaping their size, behavior, and habitat distribution. Understanding how climate influenced dinosaur development helps us uncover their survival strategies and eventual extinction.
Dinosaurs ruled the Earth for over 160 million years, adapting to various environmental changes. However, the climate played a significant role in their evolution, shaping their size, behavior, and habitat distribution. Understanding how climate influenced dinosaur development helps us uncover their survival strategies and eventual extinction.
The Mesozoic Climate: A Changing World
 The Mesozoic Era, the "Age of Dinosaurs," spanned three major periods: the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous. Each period had distinct climate conditions that influenced dinosaur evolution.
The Mesozoic Era, the "Age of Dinosaurs," spanned three major periods: the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous. Each period had distinct climate conditions that influenced dinosaur evolution.
Triassic Period (252-201 million years ago): The Earth was mostly hot and arid with vast deserts. Pangea, the supercontinent, dominated the planet, leading to extreme temperature fluctuations.
Jurassic Period (201-145 million years ago): A more humid and tropical climate developed, with lush vegetation supporting larger herbivorous dinosaurs like Brachiosaurus and Stegosaurus.
Cretaceous Period (145-66 million years ago): Although still warm, the climate began to cool slightly, with distinct seasonal changes. This period saw the rise of diverse dinosaur species, including Triceratops and Tyrannosaurus rex.
How Climate Shaped Dinosaur Evolution
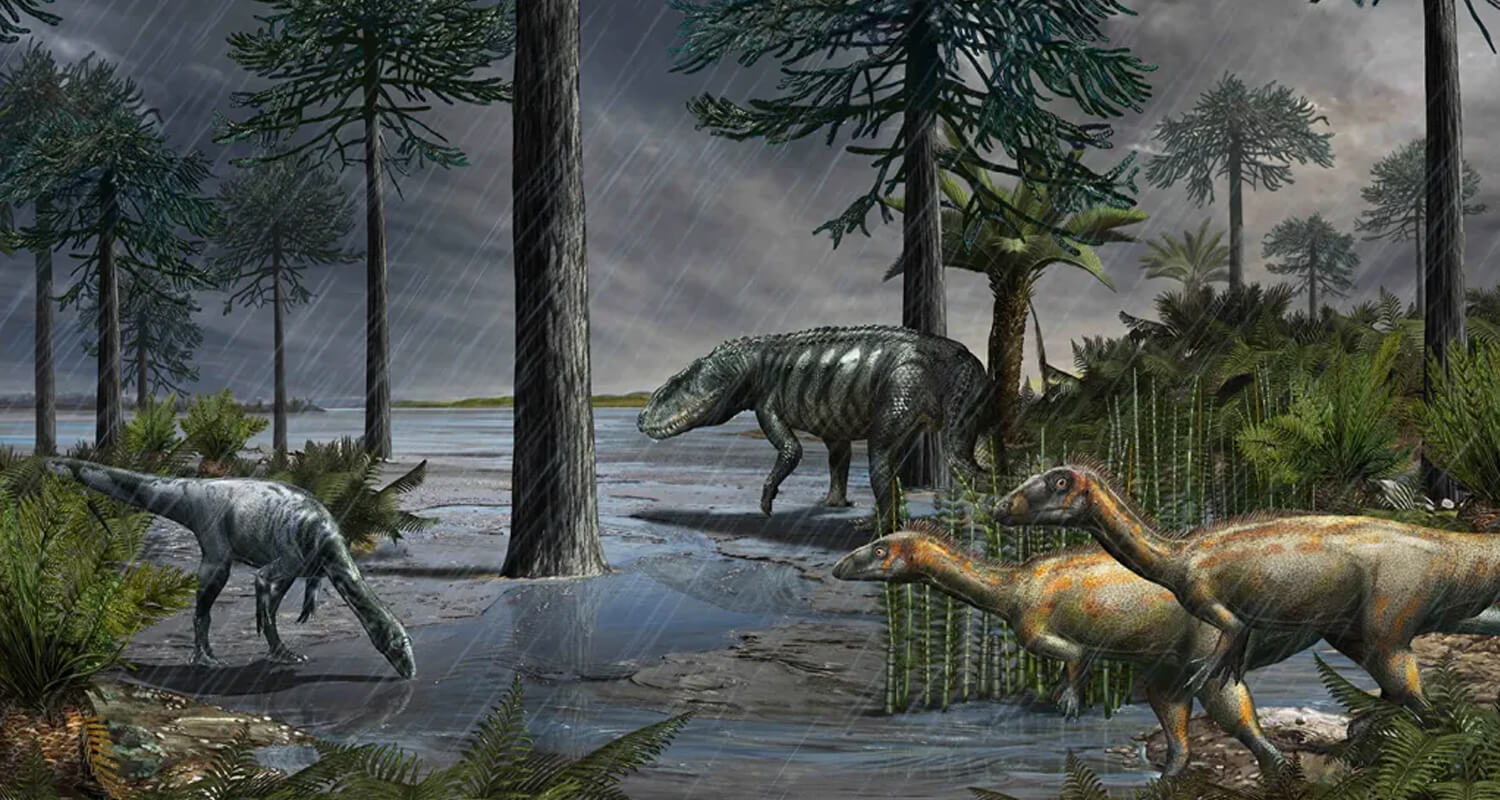 Climate directly influenced how dinosaurs evolved over millions of years:
Climate directly influenced how dinosaurs evolved over millions of years:
Triassic Adaptations: Early dinosaurs, like Coelophysis, were small, lightweight, and bipedal to survive in hot and dry conditions.
Jurassic Adaptations: The increase in humidity and vegetation allowed large herbivores and their predators to grow in size. Dinosaurs like Diplodocus and Allosaurus thrived in this environment.
Cretaceous Adaptations: Cooler temperatures led to more diverse dinosaur species, including feathered dinosaurs such as Velociraptor, which adapted for different ecological niches.
The Role of Climate in Dinosaur Migration and Adaptation
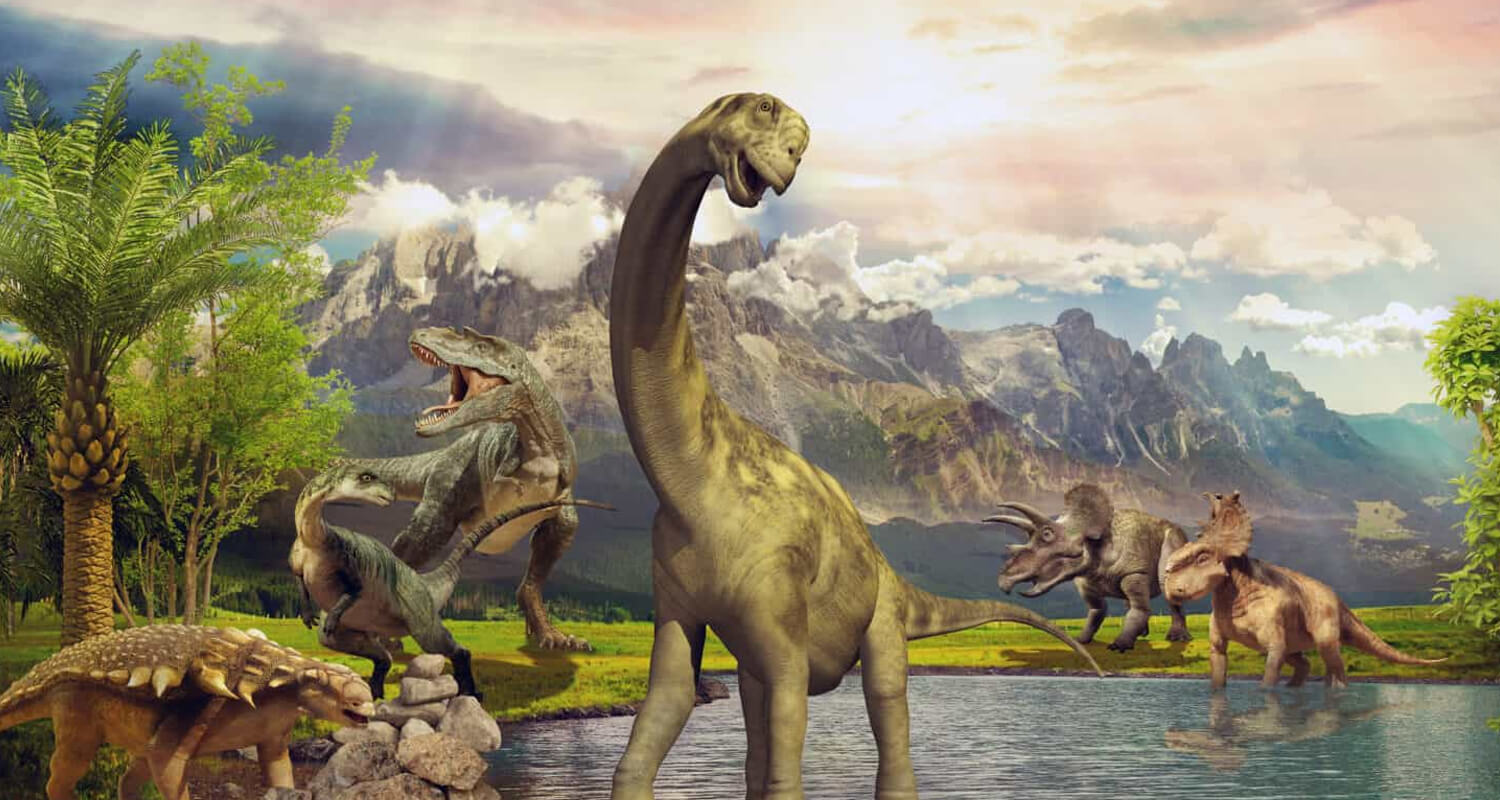 Changes in climate influenced dinosaur migration and adaptation strategies:
Changes in climate influenced dinosaur migration and adaptation strategies:
Polar Dinosaurs: Some dinosaurs, like Leaellynasaura, lived in polar regions and adapted to long periods of darkness and cold temperatures.
Desert Dwellers: Dinosaurs such as Nothronychus developed unique features to survive in arid environments.
Seasonal Adaptations: Certain dinosaurs evolved seasonal feeding patterns or migration habits to cope with environmental changes.
Climate Events That Led to Dinosaur Extinction
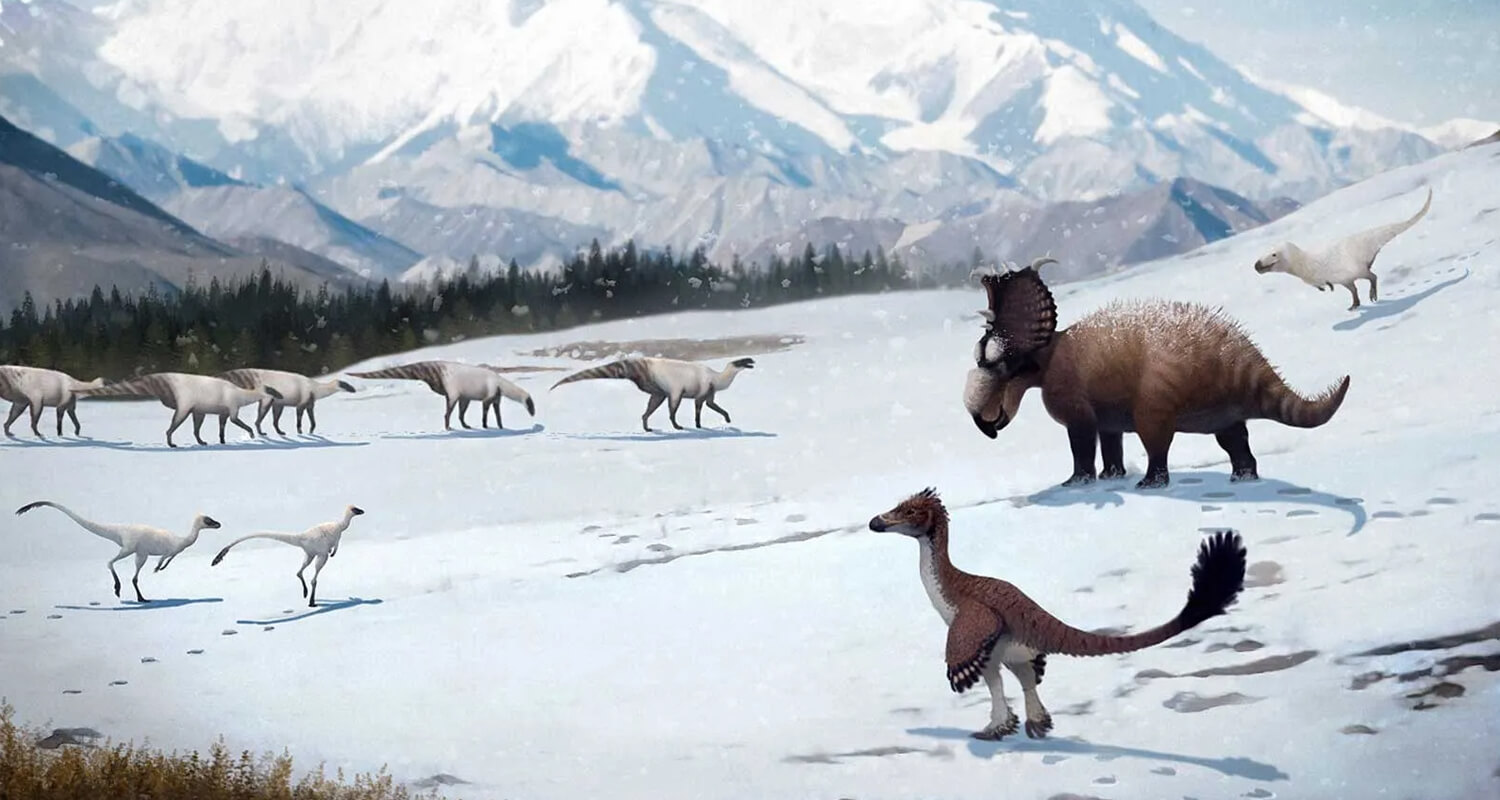 While dinosaurs adapted to various climate shifts, some catastrophic events ultimately led to their downfall:
While dinosaurs adapted to various climate shifts, some catastrophic events ultimately led to their downfall:
Volcanic Activity: Massive volcanic eruptions released greenhouse gases, leading to global temperature fluctuations and habitat destruction.
Asteroid Impact: Around 66 million years ago, a massive asteroid struck the Earth, causing fires, tsunamis, and blocking sunlight. This led to a rapid temperature drop, disrupting ecosystems and food chains.
Climate Disruption: The combination of volcanic activity and the asteroid impact created an unstable environment that dinosaurs could not survive.
The Legacy of Dinosaurs and Climate Change Lessons
 Studying dinosaur evolution in response to climate change offers valuable lessons for today:
Studying dinosaur evolution in response to climate change offers valuable lessons for today:
Climate Adaptation: Dinosaurs thrived by adapting to shifting climates, just as modern species must adapt to current climate change.
Mass Extinctions: The dinosaur extinction event shows how rapid climate shifts can dramatically affect biodiversity.
Ecosystem Preservation: Understanding past climate changes helps scientists predict and mitigate the effects of global warming today.
Conclusion
 Climate change played a crucial role in the rise, evolution, and extinction of dinosaurs. Their ability to adapt to different environments allowed them to thrive for millions of years, but extreme climate events ultimately led to their demise. By studying their history, we gain insight into how climate affects life on Earth and the importance of preserving our planet's ecosystems today.
Climate change played a crucial role in the rise, evolution, and extinction of dinosaurs. Their ability to adapt to different environments allowed them to thrive for millions of years, but extreme climate events ultimately led to their demise. By studying their history, we gain insight into how climate affects life on Earth and the importance of preserving our planet's ecosystems today.











